It’s not uncommon for your computer to fail to boot before reaching the BIOS menu when you first turn it on. Computers perform a procedure known as POST (power on self-test) every time they are turned on.
Before loading the operating system, POST validates that all of the system’s hardware is functioning properly. The machine will not boot if it fails the POST test.
If your computer won’t post, this troubleshooting guide is for you. You can try the steps described here to see if your computer can get back up and running.
You may also like to read about how many years Should a Desktop Computer Last?
What is computer POST?
POST, or Power-On Self-Test, is the first checkpoint of a computer’s power-on purpose to identify if there are any hardware-related issues with the computer. A computer is not the only device that performs POST sequence at startup.
For example, after being turned on, some electronics, medical devices, and other devices can perform similar self-checking sequences to ensure everything is functioning properly.
It makes no difference if you simply restart your computer or switch it on for the first time in a few days. POST will be executed every time you turn your PC on.
POST sequence is independent of operating systems. This is because testing is conducted by the system’s BIOS rather than any loaded software. To run POST, you don’t need an operating system installed on your hard drive.
It verifies the presence and operation of basic system devices such as processors, storage devices, peripherals, and other hardware.
The machine will continue to boot after the POST, but only if it completes correctly.
Related contents you should read about how cold can a Computer Get?
How to determine whether my computer is facing POST error or not
Before resolving any POST-related problem, it is important to verify that the issue occurring is most certainly related to the POST sequence. Due to the fact that POST starts right at startup, it is highly likely to consider other startup issues as POST-related problems.
You should look for any sign of power in your computer first. You can hear a single beep or a succession of beeps, some of which may be short, while others may be long. It’s possible that you don’t hear anything and merely see a power light. Your computer’s fans may also be whirling, but nothing else is happening.
Errors caused by almost anything that prevents the computer from booting will be flagged by your system. POST codes and beep codes with on-screen error messages are examples of errors that can be identified during internal testing of a computer.
POST failure is likely if you have any of the mentioned symptoms. You can use motherboard beep codes to narrow things down if you’re stumped. This allows for a more effective and time-efficient solution.
Search for the error code on the motherboard manual to find out the exact cause of the POST error.
Instead of a text-based error message, POST failures on macOS machines are typically shown as an icon or other image. During POST, some errors may go undetected, or the error code might get hidden by a computer manufacturer’s emblem.
Some more guides on how to tell if Your Computer Supports Dual Monitor?
What should I do if my PC has any POST error?
If you see symptoms of a POST error, you can troubleshoot your PC by following a list of structured steps. Make sure that you know how to handle the hardware components before trying to disconnect anything.
Here are the things that you can do if you are facing a POST error on your computer:
1. Identify the beep code
Your motherboard’s manufacturer employs POST codes and beep codes as visual and acoustic indicators to convey the results of internal hardware tests. You can utilize these signals to identify hardware problems that may delay your computer’s turn-on.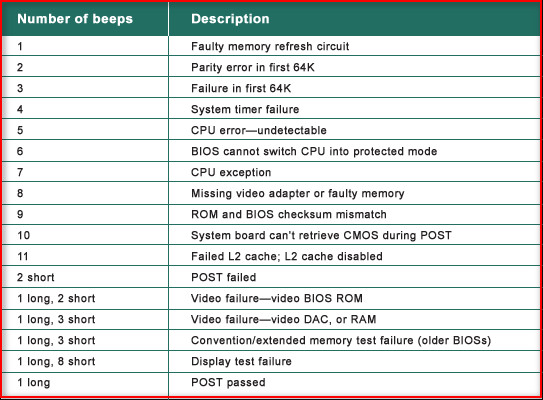
POST codes are usually two digits representing when the system faced a hardware issue while booting, which can often help pinpoint the problem’s location.
For example, RAM troubleshooting would be a good place to start if the POST code indicated a memory initialization error.
Hexadecimal displays commonly found on motherboards can show the code and help the user figure out where to begin the diagnostic process.
Alternatively, a POST test card that plugs into a PCIe slot and shows the code can be purchased if your motherboard lacks an integrated display.
Beep codes are analogous to POST codes in terms of sound. If it does, you may hear a sequence of beeps while your computer starts up.
Each motherboard manufacturer utilizes a separate set of codes for these indicators, which can be helpful. Look up the codes your motherboard manufacturer uses in its literature or online to see if you can locate the source of the problem you are experiencing.
Also related to this guide about Is My Computer Using My Graphics Card?
The table below shows the many types of common beeps and their associated meanings:
| Beep type | Associated meaning |
|---|---|
| One single short beep | POST complete, System is OK |
| One long beep followed by one short beep | Board error |
| One long beep followed by two short beeps | Display adapter error |
| One long beep followed by three short beeps | Enhanced Graphics issue |
| Three long beeps | Problem with Keyboard card |
| Two short beeps | POST error: Error code can be found on the screen. |
| Continuous beep | PSU, System board, peripheral, etc., issue |
2. Remove the expansion cards
An expansion card is an accessory used to add functionalities to the system through the expansion bus of the motherboard. These include sound cards, graphics cards, network cards, etc.
All these expansion cards are utilized to improve the functionalities of their unique functions. For example, an additional graphics card is utilized to enhance the video quality of games & movies.
However, these extension cards could induce an undetectable fault in your Windows computer and might cause POST issues. Hence, disconnect all the expansion cards from your system first.

Unscrew all the cards that are hooked into the motherboard. Remove them all by lifting them evenly straight up and level.
If you have multiple expansion cards, remove all of them, and connect them one after one to see whether any specific card is causing the problem.
Read more on why is My Computer Downloading so slow?
3. Check connections
The power cable and all other connectors should be in good condition. Do a thorough check of all wires that connect the keyboard to the storage drive, the graphics card, and the BIOS battery.
If one or more wires are damaged or filthy, this could be the root cause. The problem may be remedied if you switch it out with a fresh one.
Ensure the screws on both ends of the video and power wires are tightened. Use a different outlet for your power wire and a different port for your graphics card.
If the problem persists, try a different cable to see if it is damaged. Ensure the adapters you’re using are in good condition and utilized correctly.
4. Remove external disks and USB devices
If you can’t figure out what’s wrong with the computer using the beep code (or if you don’t hear one), shut it down. Disconnect the motherboard’s IDE, SATA, SCSI, and other data cables.

Try restarting the computer and allowing it to fully boot up. Connect each USB device and disk one at a time to identify the problematic device. A faulty cable connection is another possibility in some cases.
5. Reset the BIOS to factory settings
The BIOS needs to be cleared next. Resetting the BIOS to its default settings involves consulting your system’s manual or contacting the system support staff for assistance resetting the CMOS.
After resetting the BIOS, you’ll be able to boot the computer properly after making any necessary adjustments based on the hardware.
After performing the preceding step, you should check your motherboard’s BIOS version if you’re still not getting a POST code.
Even if your PC doesn’t boot, you can generally upgrade your motherboard’s BIOS to the latest version. The process can vary based on the motherboard manufacturer. Consult your motherboard documentation or look online to ensure you have the most recent BIOS version for your system.
6. Check the CPU and motherboard
Now that you’ve double-checked all of your connections, you can go on to further in-depth investigation. Check the CPU and the fan first.
The system will make extra beeps if the CPU isn’t installed correctly or if the plastic guard isn’t properly removed when the CPU is installed. In this case, ensure that the CPU is functioning properly and that the plastic guard is removed.
If the computer doesn’t switch on despite the power supply connections being OK, the motherboard may be the problem. Open the computer’s case and inspect the motherboard for signs of damage. Check the capacitors for bulges or blown ones.
If you performed soldering operations, the soldering component might have linked two or more places on your motherboard. The computer may be unable to power on or boot if the connections are not correct.
7. Seek professional help
The computer will need to be serviced, or some components will need to be replaced in some cases of POST errors. If you are not an expert in performing the repairs yourself, I recommend seeking professional help.
Asking for professional help will make things easier for you, but you will likely pay a large amount for that favor.
Conclusion
As soon as a computer is turned on, it is subjected to Power-On Self-Test (POST) sequence. In some cases, looking at the error codes will help you figure out the cause of the issue. The results of hardware tests are displayed visually and audibly using POST and beep indicators.
The meaning of typical beeps and error codes have been explained in the article. Examine the motherboard for signs of damage. Professional help is recommended if you are not an expert in the field.
So, did you find this article helpful in resolving POST issues on your computer?



