You might wonder if you are getting the maximum speed from your ISP (Internet Service Provider) or experiencing speed drops as your internet becomes slower than usual.
Do you think your modem is affecting your internet speed or if it can make your speed faster?
A modem is your gateway to the internet and influences your internet speed, but it is a bit more complicated than you think.
In this guide, you can learn all about how your modem works and the effects it may have on your internet speed. It has all been explained so that it is not too complicated for you to understand.
So keep reading to learn about modems and how they affect your internet speed.
Follow our guide to fix Internet disconnects when downloading large files.
How Does A Modem Work?
Your internet service provider sends analog data signals connecting your devices to the internet. A modem is a device that translates those analog signals into digital signals to make them understandable to your devices. Otherwise, you won’t be able to access the internet using your devices.
A modem is a must-have if you get an internet connection. Your ISP is the one who usually provides this box-like device when you subscribe to one of their internet plans.
Without a modem, you won’t be able to do anything with an internet connection.
An internet connection is a series of analog signals sent to your computer. Data, in the form of signals, are sent and received by your computer. Now, your computer or any other device only understands digital ‘O’ and ‘1’, but the analog signals sent by your ISP have continuous values. This is where a modem comes in.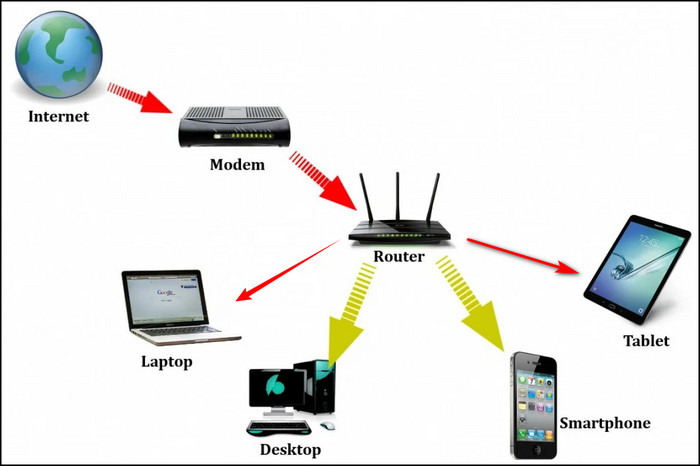
The task of a modem is to convert or translate the analog signals you receive from your ISP into digital values and then send those values to your computer.
Many modern computers and mobile devices do not require external modems to connect to the internet. Then how do they form internet connections if they don’t have a device that translates the analog signals? Well, they do have integrated modems that function similarly to an external modem.
For example, your phone has an integrated baseband processor that does the same job as a modem.
That is why you can connect your phone to the internet whenever and wherever you are by receiving signals from your teleservice provider.
The speed of your internet connection depends on your subscription plan with your service provider, but your modem also has some effects on it as well. In the later sections of this guide, you can learn how your modem affects your internet connection speed.
Check out the easiest way to can a Modem be used as a router.
Does Your Modem Affect Your Internet Speed?
Your modem affects your internet speed. Your modem cannot make your internet connection faster. Older modems can make your internet slower. Your ISP’s maximum speed depends on your ISP.
As your modem is the device translating the signals sent to your computer, much depends on how fast it can do the job.
The analog signals from your ISP come to your device through the modem, where they are translated first. If your modem converts these signals slower than they are received, you won’t be able to use the full potential of the connection’s speed. This is where the bottleneck is created.
For example, if you have subscribed to a 100 Mbps data plan with your ISP, but your modem only translates at 80 Mbps, you will only be getting 80 Mbps speed.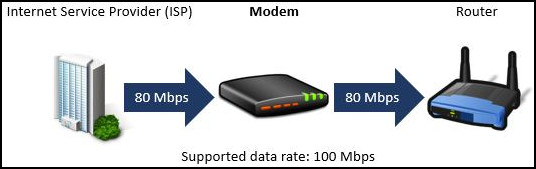
Simply put, a bottleneck is created when your modem converts data at a slower rate than your ISP sends you the data. So, your modem may be slowing down your internet.
It is impossible to make your ISP’s internet speed faster than they already provide you by using a modem. So, conclusively, your modem cannot make your network faster, but older or low-spec modems can make you experience a slower speed than what you are supposed to get from your ISP.
Some specifications within a modem determine its data conversion potential. These are factors to consider in figuring out your modem’s effects on internet speed.
In the next section, you can find out everything you need to know about the things in a modem and how they affect your internet speed.
Read more on when to replace Modem & How Long Does it Last.
What Factors In Modems Affect Your Internet Speed?
Certain specifications in your modem, like the hardware, firmware, ports and cables, DOCSIS version, etc., determine whether your modem will convert data quickly or slowly. The better the components within your modem, the faster it will be, letting you enjoy peak internet speed.
Your modem is a computer with a specific function. So, similar to a computer, its performance depends on its hardware and software.
The data plan you have with your ISP is the maximum internet speed you can achieve. Although, this speed can be reduced if your modem is not specced enough to translate data at a higher rate than the rate at which it receives the data from your ISP.
Your modem must translate data at the same or higher rate for maximum internet speed than your ISP.
The factors that affect the data translation rate of your modem are:
1. Modem hardware: The performance of your modem dramatically depends on the technology used to build its hardware.
The technology can become outdated quickly; if you are using an old modem, it isn’t capable of converting data at a fast rate. As a result, you might miss out on a lot of internet connection speed.
2. Firmware: As mentioned before, your modem is like a computer. So, essential software called firmware is required to run it. It is suggested to have the updated firmware on your modem, or else it won’t be compatible with the services provided by your ISP. The firmware can have bugs that may bottleneck your internet speed if it is not updated.
3. Connection ports and cables: Your modem’s ethernet ports and cables influence your internet speed. See to it that your modem has the ports that support higher speeds and use the right cables.
4. DOCSIS version: There is an international data transfer standard called Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification through coaxial cables. The latest version of DOCSIS, DOCSIS 3.1, can transfer data at the rate of 10 Gbps. This is way faster than previous versions. If your modem supports the latest DOCSIS version, it will let you use your internet connection at maximum speed.
5. Distance of router: If you are using a router along with your modem for a Wi-Fi connection, the speed of your internet is also affected by the router.
Routers send wireless signals over an area to your device for transferring the data connection. These signals get obstructed or diminished if there is a reasonable distance between your device and the router. Moreover, physical objects like furniture and concrete walls block the signals. This can reduce your internet speed by a lot.
If you think your modem lacks any of these specifications mentioned above, you can change it by contacting your ISP and asking them to provide you with the newest models.
Also read how to fix arris Modem keeps resetting, You may also like do you need an ethernet cable for WiFi, Check out the easiest way to Fix Internet Goes Out Same Time Every Day
Conclusion
Internet connection is streamed through a modem before it can reach and be recognized by your device. If the path of streaming the data connection isn’t wide enough, fewer data can pass through in a given amount of time. The path is, obviously, a metaphor for the specifications of your modem.
Going through how your modem affects your internet connection speed, you can find out if your modem has any negative effects on the internet speed.