Have you ever wondered which materials or components are used to build a motherboard?
You might be tempted to learn how the motherboard is made which connects all the PC components.

Well, I will tell you everything you need to know about motherboard materials and manufacturing in this post.
Keep reading as this post will satisfy your curiosity about motherboards.
What Are Motherboards Made Of?
Motherboard components can also consist of gold, silver, steel, aluminum, silicon, solder, and plastic.
Let’s discuss in detail the various raw materials that motherboards are made of.
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) made of sheet of fibreglass fabric coated with epoxy resin and copper make up the majority of motherboards. Fiberglass provides insulation, while the conductive paths inside the component are formed by copper.
Epoxy resin is applied to a fiberglass sheet during the production process, and the resin is heated. To complete the curing of the resin, heat is applied.
It is exposed to heat until the resin is partially cured. The sheet is called or also known as the Prepreg.
Multiple sheets of prepreg are stacked together to form a laminated sheet until the desired thickness is achieved. They are placed in a heated press to fully dry the resin after being applied to both sides of the stacked prepregs with thin layers of copper.
Check out our separate post: Do I Need to Install Motherboard Drivers.
Both sides of the copper-clad laminate sheet stick together. Copper forms the conductive pathways in the motherboard. 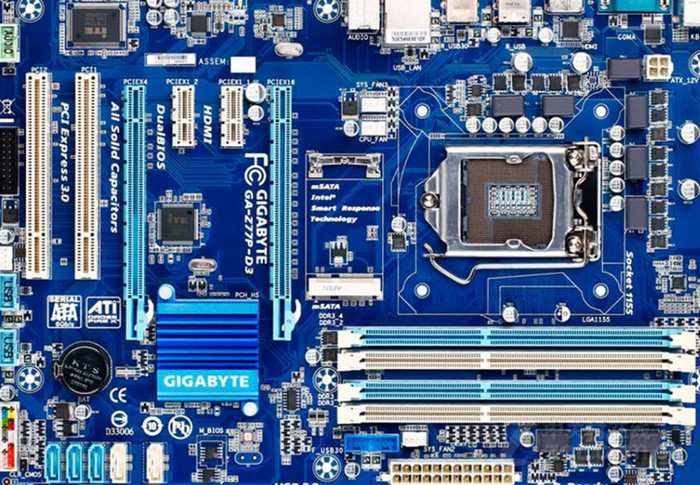
A PCB should contain as many layers as possible since this will allow for more direct signal lines from one metal component to another.
Although sheets of copper foil and fiberglass are the two primary materials utilized in a motherboard, there are also additional materials. For example:
- Gold is used for IC bond wires and electrical connections.
- Steel is used for some connection housings.
- Aluminum is used for the CPU cooler.
- Silicon is used for IC.
- Ceramic compounds are used for tiny capacitors.
- Plastic is used for the majority of connections, RAM slots, and expansion slots.
Let’s take one step back and ask ourselves, what is a motherboard? The motherboard is where all the PC components are attached. It functions as the central nervous system of the PC.
The CPU socket, RAM slots, USB ports, and disk drive slots are placed onto a motherboard. It offers connections for different peripherals and permits communication between the main electronic parts of the system.
The PCB’s (Printed circuit board) name derives from the fact that it serves as the communication medium for all components. 
It is either connected directly or indirectly to every component of the PC. A motherboard’s floor is a solid sheet of non-conductive material covered in traces, which are small layers of copper or aluminum sheets. These traces form the connections between various components.
Motherboards also have many connections and slots. These are used for connecting additional components to these circuits.
For example, the PCIe slot is used to connect the GPU, the RAM slots are used to attach the RAM sticks, etc.
In a laptop, the motherboard is located below the keyboard, but it is often placed vertically in a desktop computer.
Here’s an epic guide on 7 ways to fix BIOS is updating LED firmware on Asus Motherboards.
What Are The Different Parts of a Motherboard?
A motherboard comprises several parts, including CPU sockets, I/O ports, BIOS, CMOS, and even its own chipset. Memory slots and power connectors are also considered essential parts of a motherboard. The voltage regulator module (VRM) plays a vital part in a motherboard.
Here is a brief discussion of those parts to make up a motherboard:
1. CPU Socket
The CPU socket is where you put the CPU, and communication between the CPU and other parts happens through the socket. Since CPU manufacturers employ proprietary designs, your motherboard and CPU must be compatible.
The motherboard must match the exact CPU socket type.
2. BIOS and CMOS
BIOS stands for Basic Input Output System. It is software installed into the motherboard chipset. All motherboard settings and critical information needed to start the PC are saved in the BIOS. The BIOS also controls the boot sequence, which is needed to start a computer.
When the system shuts down, the CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) battery maintains all information unchanged.
Because the CMOS battery is easily accessible, you can replace it to reload the BIOS. Just turn off the motherboard and unplug it from the power supply.
3. I/O Ports
Depending on your motherboard specifications and internal components, there are many color-coded ports at the rear of the motherboard.
Here is a list of the I/O ports:
- PS/2 ports for older keyboard or mouse.
- HDMI, DP, or VGA ports for display and graphic.
- USB ports for connections to external devices and data transfer.
- RJ45 ethernet port for internet access.
- 3.5mm ports for microphones, loudspeakers, and headphone jack.
Many modern motherboards come with buttons or switches at the rear panel to flash the BIOS.
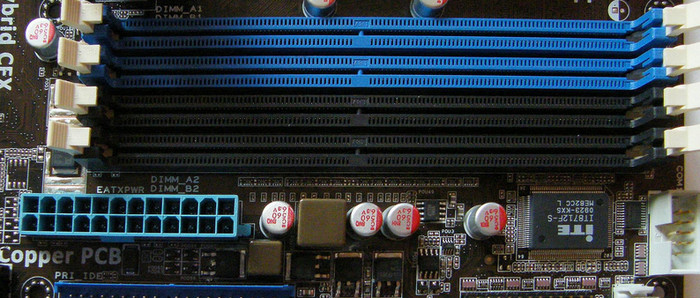
4. Memory Slots
The RAM modules are inserted into the Random Access Memory (RAM) slots in the motherboard.
The RAM slot is always adjacent to the CPU to ensure fast communication between the PC’s memory and CPU.
Every pair of slots is designed to operate within the same frequency band. For the most outstanding performance, putting two sticks of RAM in slots that are the same color is recommended.
Typically, experts refer to this as a dual-channel configuration. You can also go quad-channel by putting a stick in each of the four slots (if your motherboard has them).
Check out the easiest way to fix Motherboard HDMI No Signal.
5. M.2 and SATA Connections
The SATA connection allows you to connect the HDD (hard disk drive) and SSD (solid state drive) present in the motherboard. Older motherboards had IDE connections, but they are obsolete now.
M.2 devices using the PCIe interface may transmit data six times quicker than a typical SATA SSD. So newer motherboards also have M.2 slots for faster SSDs.
Compact devices like laptops and tablets may now have high-performance storage thanks to M.2 SSDs. Since M.2 devices are increasingly becoming a standard component of desktop PCs, they are often regarded as the greatest storage options.
6. PCIe Expansion Slots
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) is a high-speed expansion bus standard for motherboards. Multiple of these expansion slots are present in the motherboard.
GPU is the main component attached to the expansion slot, but you can use them for other external devices like a WiFi module, USB or sound cards, etc. A large motherboard usually has three expansion slots.
7. Northbridge And Southbridge Chips
The task of the northbridge chip is to communicate with the CPU and performance-sensitive components. But, the northbridge chip is built into the modern CPUs.
The southbridge communicates with less performance-sensitive components such as USB and storage.
8. Fan and ATX Power Connectors
A motherboard fan connection is a three or four-pin connector that supplies electricity to your case fans.
A three-pin motherboard fan connector frequently contains red, yellow, and black wires on the side of the PC fan, depending on the model and the manufacturer.
The yellow line communicates the fan’s RPM to the computer, while the black wire conducts electricity.
The Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) function on a four-pin connection makes it possible to change the fan speed.
The fan only receives the amount of power necessary to run at the speed you specify because of the PWM’s ability to cycle the power on and off so quickly.
SYS_FAN and CPU_FAN labels are used in motherboard manuals to describe fan connections. At least two female connections on each motherboard accept power from the PSU.
For general power distribution to the motherboard, a 24-pin ATX motherboard (advanced technology extended) connection is utilized. The 20 or 24-pin female connectors is the largest connector on the motherboard. 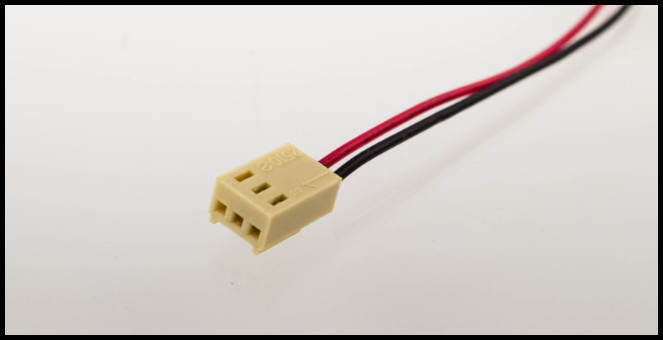
A separate 8-pin connection additionally powers the CPU. There are power connections for the GPU as well.
9. VRM (Voltage Regulator Module)
Similar to a PC’s power supply unit, the voltage regulator module (VRM), also called a Processor Power Module (PPM), regulates voltage.
Your motherboard’s VRMs, control how efficiently power is managed.
They often lower the voltage to supply the precise quantity the CPU needs. Chokes and MOSFET are the two parts that make up the VRM. 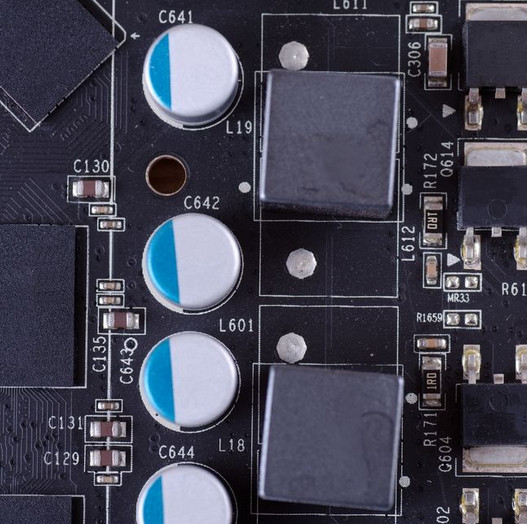
The MOSFETs (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors are flat, tiny components often positioned around the CPU. The MOSFET is in charge of supplying the CPU with the necessary quantity of electricity.
When a sudden voltage spike occurs, often chokes beside the MOSFET stabilize the currents and capacitors. Therefore, additional chokes in a VRM result in a CPU current that flows more steadily.
The best VRMs are those having six or more chokes if you intend to overclock your CPU. Be cautious to keep VRMs cold because they frequently overheat.
How are Motherboards Manufactured?
This will be a relatively simplified explanation of what occurs because hundreds of different equipment and stages are involved in manufacturing motherboards. But it will provide you with enough basic idea about how are motherboards made.
Fiberglass and copper are the two main materials forming the base of a motherboard. The basic printed circuit board is known as PCB. First they’re made by joining layers of fiberglass impregnated with epoxy resin and heated to form a prepreg. Then copper is applied to the top and bottom layers to bond together.
The polymerised portions of the photoresist is applied to the top layer to safeguard the upcoming copper conductive pathways routes on the PCB.

The board with photo-resist is exposed to ultraviolet light. Then the board is immersed in a chemical solution to develop image.
During manufacturing, the remaining copper circuitry not covered by the chemical called photoresist are etched away. Thus the basic motherboard PCB gets stripped away of any installed chips or other essential parts.
The copper foil are applied to help in conduction. Boards are washed to remove residue. Holes are drilled through the board to allow through-hole components.
The next step is installing most of the motherboard’s components using SMT (Surface Mount Technology).
After that, a Dual In-Line Package (DIP) production line is used to assemble capacitors and all hand-mounted components.
As it turns out, components are mounted by hand in addition to machine installation to mount several components on the motherboard. Even today, producing a motherboard involves a lot of machinery and experienced workers.
Before the motherboard leaves the plant, it must undergo extensive testing by floor staff when it departs the production line.
To prevent electro-static discharge (ESD), motherboards that pass these tests are first put in anti-static bags before being padded, boxed, and sent.
These are the fundamentals of the motherboard manufacturing process.
Conclusion
I hope this post helped you understand what PC motherboards are built of and gave you a good sense of how it all comes together.
Copper and fiberglass are the primary raw materials to build a motherboard. Gold, silver, steel, aluminum, silicon, and plastic are also vastly used to in different parts.
Several parts, like I/O ports, expansion slots, RAM modules, etc., make up a motherboard.