With the release of Windows 11, Microsoft introduced new system requirements for its installation, and it’s related to security. Yes, I am talking about the Trusted Platform Module (TPM 2.0) requirement.

While that’s an excellent addition for protecting user data and keeping it secure, it also creates more questions among individuals who have different types of TPMs installed. PTT and dTPM is a good example of this.
If you are wondering whether your PC with dTPM or PTT satisfies the Windows 11 TPM requirements, you are on the right page. I asked the same question not too long ago, but it wasn’t possible to find a straight answer right away.
That won’t be the case for you if you keep reading. So, go ahead and grab some caffeine before moving to the next section.
Is dTPM the same as TPM?
Microsoft uses TPM or Trusted Platform Module, which was introduced around 20 years ago, to enhance the security of its services like BitLocker drive encryption, and Windows Hello. It does this by creating and storing cryptographic keys.
These keys can help detect whether the firmware and operating system of your device are tampered with or modified in any way.
However, after the introduction of the TPM 2.0 standard in 2016, various motherboard manufacturers, like AMD or Intel, now have the ability to incorporate the TPM capabilities into their chipsets without requiring a separate chip.
Also, check out our separate post on how to fix PC won’t go to sleep in Windows 11.
Which One is Windows 11 Compatible: dTPM or PTT?
Windows 11 is compatible with both dTPM and PTT-enabled computers. This is because both of these are a form of TPM. To understand this better, you need to have some background on dTPM and PTT.
So, what are dTPM and PTT, then?
Well, dTPM is the original TPM that requires a separate chip to be installed in the motherboard. If you see dTPM on your BIOS window, it should tell you that your PC has an unused slot where you can install a hardware TPM.
That leaves us with PTT and fTPM. These are more commonly used these days since they don’t need to be physically present on your computer.
Since fTPM and PTT are used by the majority of PCs and laptops nowadays, it’s natural that Windows 11 would support this. There was a risk of dTPM not being supported on Windows 11, but Microsoft came through and enabled the support to avoid losing market share.
How Can You Tell If Windows 11 TPM 2.0 Is Compatible with My Computer?
There are multiple working methods that I personally tested to check whether TPM 2.0 is compatible with my computer, and I am sure they will work on your PC as well.
Before looking at the methods, you need to make sure your laptop is relatively new. That’s because there is no point in testing for TPM if your computer is 8 or 9 years old. Those laptops won’t support TPM 2.0.
Another point to consider before moving forward is that there is no need to check if TPM 2.0 exists on your system if you are already running Windows 11. Since Windows 11 needs TPM to run, your PC will already support it.
Follow these steps to tell if Windows 11 TPM 2.0 is compatible with your PC:
1. Install the PC Health Check App
Microsoft introduced a new PC health check application that is mainly used to detect issues within your PC. However, after the release of Windows 11, the app was also updated to check if your PC meets the minimum requirements to run Windows 11.
As a result, the app will automatically detect if TPM 2.0 support is present on your system as part of the Windows 11 system requirement.
Follow these steps to install the PC Health Check app:
- Click this link to start downloading the latest version of the app immediately.
- Double-click on the downloaded file to start the installer.
- Follow the instructions to install the app and set it up correctly.
- Launch the app as soon as the installation is completed successfully.
- Click the Check Now button at the top to let the app scan your system.
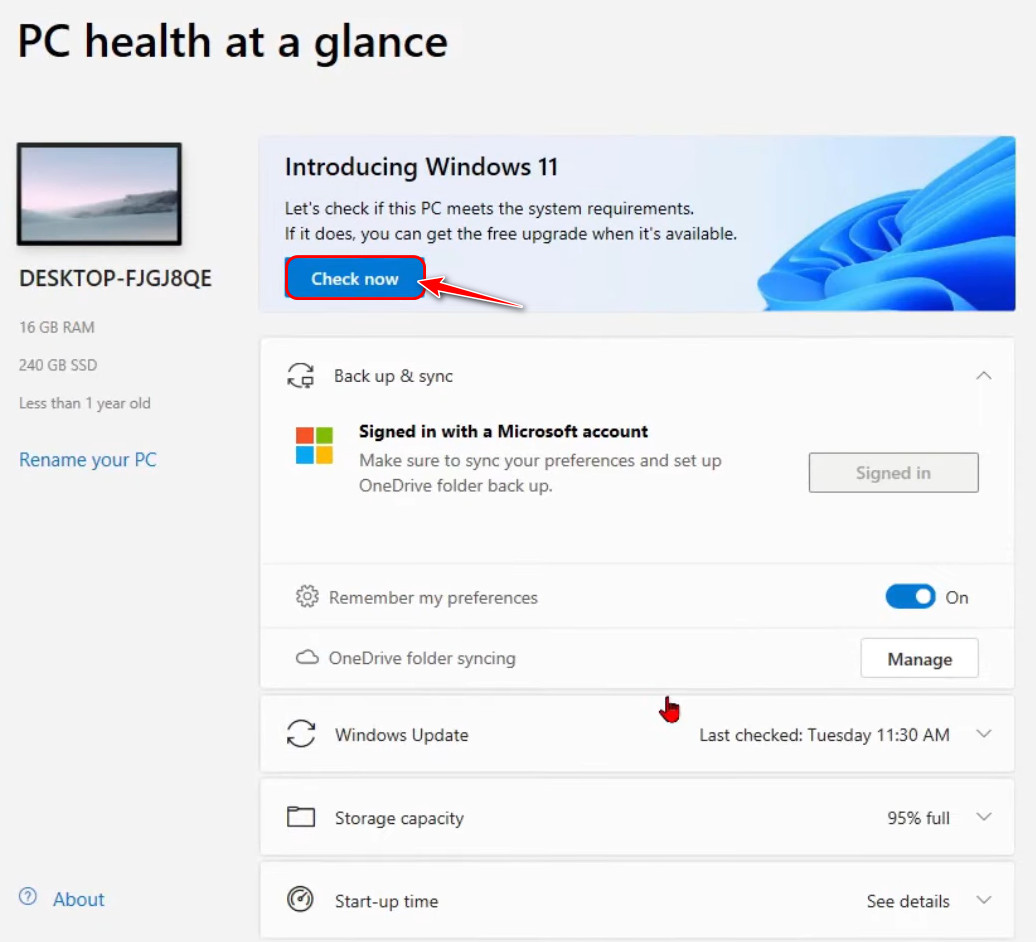
- Wait for a while for a message to appear. If it says ‘This PC meets Windows 11 requirements’, your PC supports TPM 2.0 requirements.
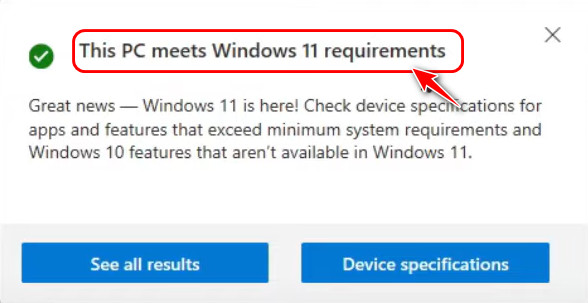
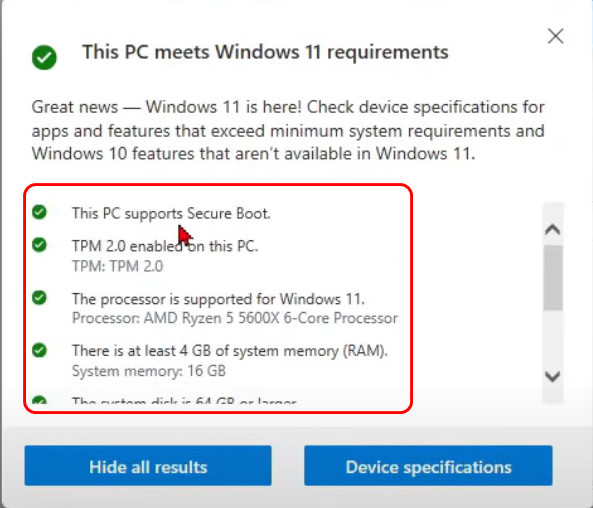
- You can also click on the See All Results button to find detailed information on which features your PC supports or which don’t work.
Check out the easiest way to install active directory users & computers on Windows 11.
2. Check Security Devices
As you already know, TPM 2.0 is used to upgrade the security of several Windows services, and as a result, you can find it under security devices in the Windows Device Manager if it’s installed on your PC.
Follow these steps to check security steps:
- Press the Windows and X keys at the same time to launch a context menu.
- Select Device Manager from the list of options.
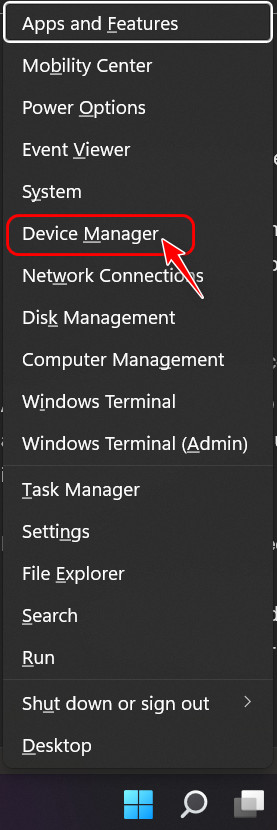
- Locate Security Devices once the window opens and double-click on it.
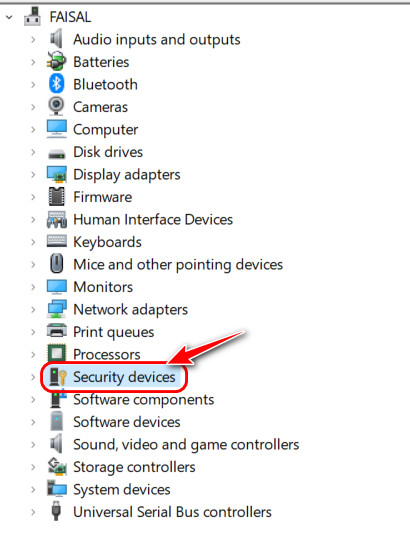
- Check if there is a device named Trusted Platform Module 2.0 under it. If it exists, your PC supports TPM 2.0.

Find out how to fix lock screen stucked on Windows 11.
3. Use Windows Terminal
Windows Terminal is Microsoft’s improved version of Microsoft PowerShell, and you can use either app to test whether TPM is installed on your device with a simple 2-word command.
Follow these steps to use the Windows terminal to test TPM installation:
- Right-click on the Start menu icon and select Windows Terminal (Admin) from the list.
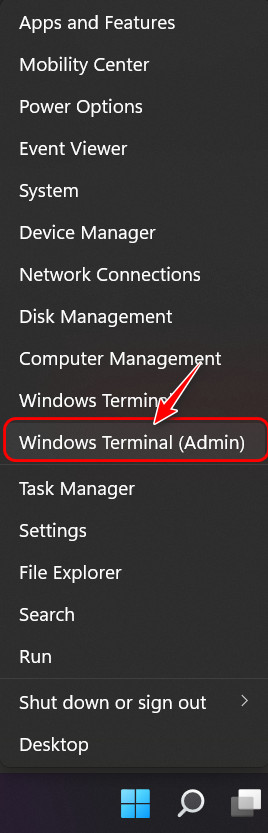
- Select Yes if any User Control window appears.
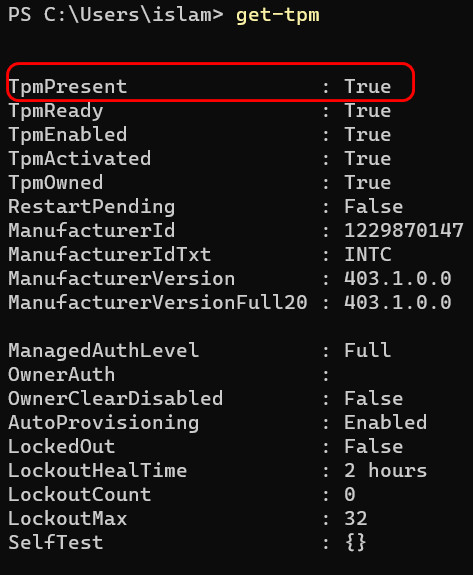
- Type ‘get-tpm’ and hit Enter once the Terminal window appears.
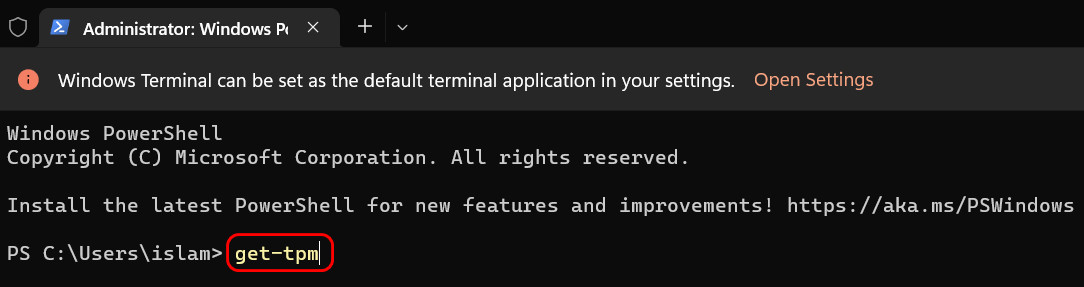
- Look for the value next to TpmPresent. If it’s True, your PC supports TPM.
4. Launch TPM
Windows has a Trusted Platform Module manager by default on all systems, even those that don’t support it.
Therefore, you can launch that application and check whether TPM is running or offline.
Follow these steps to launch TPM:
- Launch a Run window by pressing the Windows and R keys simultaneously.
- Type msc in the text field and press Enter.
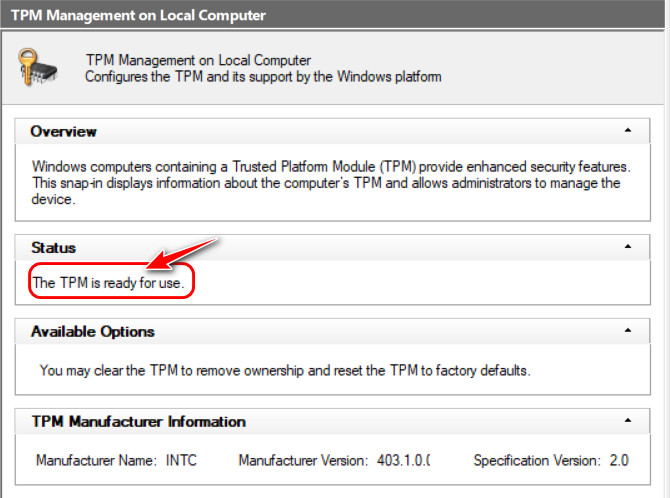
- Read the text in the Status Your PC supports TPM 2.0 if the message says the TPM is ready for use. Otherwise, you are out of luck.
Also check our exclusive tutorial on does Windows 11 support Dolby vision.
FAQ
Question: Should I enable PTT in BIOS?
Answer: Yes, you should enable PTT in BIOS to add an extra protective layer of security to your operating system. This will also allow you to encrypt data without requiring a password. Devices that don’t have TPM will also benefit from this.
Question: Can PTT replace TPM?
Answer: Yes, PTT can replace TPM. Actually, that’s the primary purpose of PTT. You see, Intel created PTT to help enable TPM on computers that don’t have a separate TPM chip, and it works flawlessly.
Question: Can I install Windows 11 without TPM?
Answer: No, officially, you cannot install Windows 11 without TPM support. However, you can bypass the minimum requirements and install Windows 11 without it. This is not recommended because you might face issues.
Question: Can you install a TPM chip?
Answer: Yes, you can install a TPM chip if your PC doesn’t come with one. Before doing that, you need to check if your PC has available slots. This can be done by checking if your PC has any dTPM in BIOS.
Final Thoughts
The importance of the Trusted Platform Module has been more pronounced these days ever since Windows 11 was released.
Among the various types of TPM, I discussed the 3 main types, dTPM, fTPM, and PTT, in the introductory section. That should clear up your confusion and answer the question in your mind.
The following section is dedicated to users who want to understand exactly which version of TPM their PC is running and determine whether they can upgrade to Windows 11 without issues.
I remember installing the PC health check app before installing Windows 11. Will you do the same? Let me know in the comments.