Everything that you see and do on your computer is basically data, that is, strings of 0s and 1s. The main functions in a computer system are carried out by processing this data.
While executing a function, not all data is processed at a time. The data which is not being processed needs to be stored somewhere. This is where the storage system of a computer comes in.
A computer system has different kinds of memories that store data. They differ in speed and size based on the function that they are allocated for. You can learn all about them from this guide. You will also find out where most of the data is stored in a computer.
So keep reading to familiarize yourself with a computer’s storage system.
What Are The Types Of Storage In A Computer?
A computer system has many types of memories for storing all sorts of data. They are mainly of two types: primary memory and secondary memory. Primary memory can store a lesser amount of data than secondary memory but it has a faster data transfer speed.
Primary memory and secondary memory have different and specific functions because of their dissimilarities in speed and size.
Primary memory is also called temporary memory or just memory. Their function is to store data temporarily while a process is being carried out on your computer. A lot of data cannot be processed at the same time and that is why it is absolutely necessary to have primary memory in your computer.
The high data transfer of primary memory speed makes it possible for your computer to carry out commands instantly. The data in primary memory are volatile, meaning that they are temporarily stored.
These are the different kinds of primary memory and their functions:
- Cache memory: This type of memory is closest to the processor. It is usually integrated within the CPU so that it can be instantly accessed. Cache memory is the smallest in size but also the fastest.
- RAM: It stands for Random Access Memory. This is the memory that can be directly accessed by your computer’s processor. Any running program is first loaded on the RAM from your storage memory before being executed.
- ROM: It stands for Read-Only Memory. It contains permanent data that never needs to be changed. The data is only required to be read at specific times. ROM contains the boot program of a computer that starts up the system when you turn it on.
- Virtual Memory: This memory can exist when a portion of your secondary memory is converted and used as primary memory.
Besides the memories discussed above, your computer also has secondary memory, or more commonly known as storage. Secondary memory is larger than primary when it comes to memory size but it has a significantly lower data transfer rate.
The main function of secondary memory is to store all your files, programs, images, videos, music and everything else in the form of data.
Here are the different secondary memories that are used with computers:
- Hard disk drives: Hard disk drives, or HDD in short, are the most commonly used storage devices in modern computers. They store data on a magnetic disk. Although their read/write speed is slower than that of any primary memory, they have terabytes of data space to store all the files in your computer.

- Solid state drives: Solid state drives (SSD) serve a similar purpose as HDD but they have significantly higher read/write speed. For this reason, they are more expensive than HDD. SSDs are becoming more popular nowadays and are slowly replacing HDDs as the main storage device in many computers.

- External hard disk drive: This is a popular mode of portable data storage used for carrying large amounts of data on the go. They can be accessed from any computer through a USB connection.

- Flash drive: Flash drives are very small in size and contain a few gigabytes of space for portable data storage and transfer. They are connected to computers using USB.

- Memory card: These are small in size with few gigabytes of data storage. They are mainly used for transferring media files between computer and other devices like camera or mobile phones.

- Optical memory: Optical disks are portable data storage devices of the past they aren’t very popular now but are still used for commercial purposes to sell copies of a program or game. They require an optical drive on your computer to access the data in them.

- Floppy disk: Floppy disks are an even older technology than optical disks. They are magnetic discs where data is stored. You will need a floppy disk drive to read them.

- Tape memory: Tapes are a primitive mode of portable data storage which were mostly used to store images, videos, and music in the past.
From all these types of memory and storage devices, you can probably guess by now where most of the data in your computer is stored. If you haven’t figured it out yet, read about it on the following section.
Where Is Most Data Stored In Your Computer?
Most of the data in your computer, including your operating system, programs, documents, images, videos, music, and literally everything else that you can think of are stored on your computer’s hard disk drive. Any file that you want to run from your HDD is loaded onto the RAM first.
The HDD is a computer’s main storage device but recently they are in close quarters with SSD. This is because of the rising popularity of SSDs for their high data read/write speed.
Hard disk drives store the data within magnetic disks inside the drive and need to spin a header to read or write data on the disks. It is because of their mechanical features that HDDs are slower than SSDs. Still, they are most people’s top choice to use as main storage because of their affordability and reliability.
A brief detail of how hard disks work is given on the next section of this guide.
How Do Hard Disk Drives Store Data?
Data is stored on a hard disk drive in the form of 0s or 1s. An HDD consists of an aluminum a disk, or disks, with magnetic coating. The 0s and 1s are saved on these disks as magnetic nature. This data reading and writing is done by the change of voltage.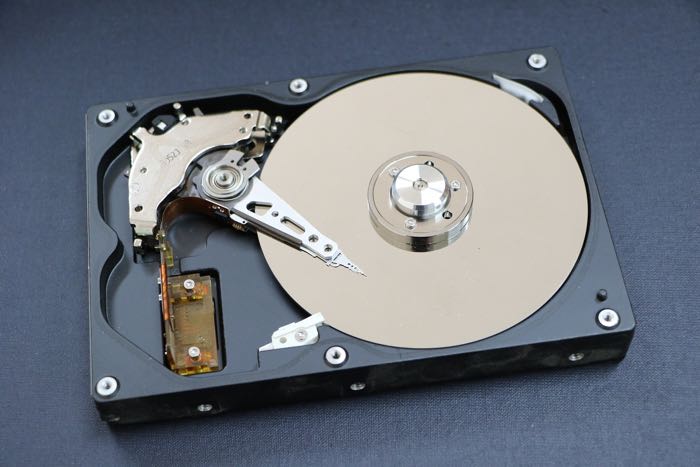 
A computer only understands binary values (0 and 1). Data is presented to a computer in the form of a string of many 0s and 1s.
Every instruction and data processed by a computer are converted to binary values beforehand.
Binary data follow a path in your computer system during processing by the change of voltage through several complex circuits. Absence of voltage means 0 and the presence of voltage means 1. This is how a computer understands our commands, and stores and processes our data.
In a hard disk drive, the varying voltage changes the magnetic nature of the disks to match the voltage. This is how your data is stored in hard disk drives.
If you want to run a program, open a document or do anything else with the data on your hard disk drive, it is first read from the magnetic disks by spinning them and moving a head that reads the data on those disks.
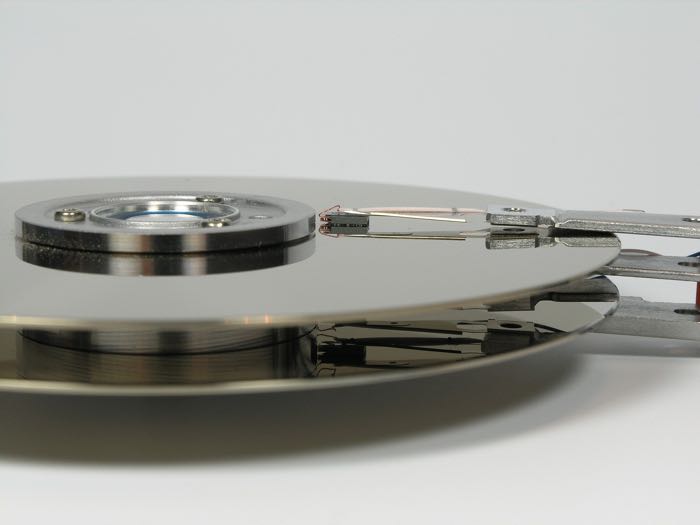

Then that data is transferred to your computer’s RAM to be accessed directly by your processor. Remember that your computer’s processor cannot directly access your HDD.
It is important to keep in mind to never bring a magnet or electromagnet in close proximity of your HDD. This will disrupt the magnetic nature of the disks and corrupt the string of 0s and 1s. You will lose your data even if one single binary value gets changed.
Give the following section a look for a short comparison between HDD and SSD.
Should You Get An HDD Or An SSD For Your Computer?
Hard disk drives (HDD) and solid-state drives (SSD) are close competitors in today’s market as a computer’s main storage device. HDDs are still very widely used but SSDs are also becoming quite popular for building high-spec computer systems.
If you are planning on getting a main storage for your computer but cannot decide between getting an HDD or an SSD, then check out the comparison between them presented here.
These are the differences between an HDD and an SSD:
- Storage size: HDD and SSD both offer same storage sizes but you can get an HDD with more storage than an SSD for the same amount of money.
- Cost: SSDs cost significantly higher than HDDs, which is a drawback.
- Read/Write Speed: SSD has amazingly higher speed than HDD because, unlike HDD, it does not have any moving parts. Data is rather stored on interconnected chips in the SSD.
- Availability: HDDs are more widely used and easily available than SSDs.
- Lifespan: SSDs tend to have a shorter lifespan than HDDs because they get exhausted after shorter number of reading a deleting cycles. So, the lifespan actually depends on how much the SSD is used. It is seen at times that an SSD may last longer than an HDD if it is rarely used.
After having considered these characteristics of HDDs and SSDs, you can now make a decision on what you should get. Then again, there is nothing stopping you from getting both of them.
Conclusion
Memory is a crucial part of every computer system. All your precious files are stored here but that’s not the only function of memory devices. They are also an important unit when it comes to the processing of any sort of data by your computer.
As you go through the different kinds of computer memories discussed in this guide, you will realize how important they are and also get to know more about your computer’s main storage device.