SVM stands for Secure Virtual Machine. This mode is provided in a computer’s BIOS to provide virtualization functionality to the user.
Are you someone who is wondering about what SVM is, how to access it, and whether or not to enable it?
If so, you have come to the right place. This article contains an in-depth guide concerning the SVM mode, how to enable it, and so on.
Let’s get started!
What is SVM mode in the BIOS?
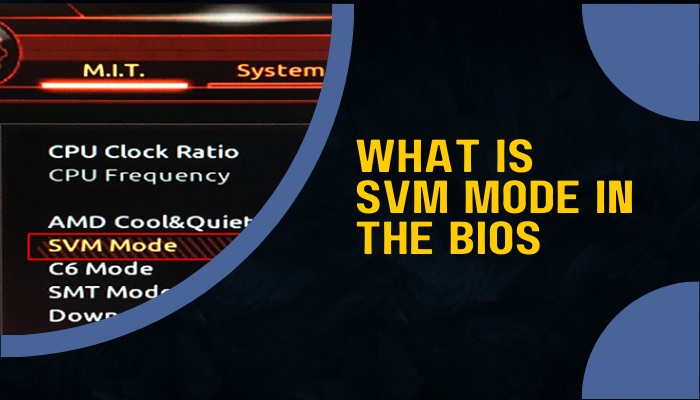
SVM Mode is an option found inside the BIOS of AMD chip-supported motherboards. By accessing this menu, you can enable Secure Virtual Machine or SVM. In addition to delivering a protected environment for virtual machines, SVM also makes it possible to gain more direct hardware access.
It enables specific BIOS options, such as higher performance when using Virtual Machines.
AMD refers to the technology as AMD-V in addition to the name SVM; hence, it is also possible that your BIOS will list it under the name AMD-V.
Is there any intel equivalent to AMD SVM mode?
If you use an Intel processor, the obvious follow-up question in your mind would be whether or not your BIOS contains a functionally identical feature.
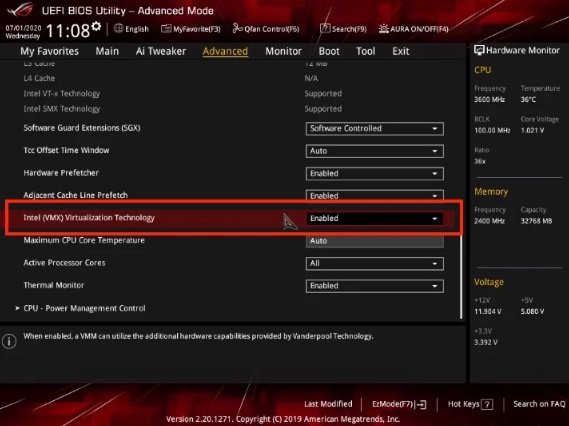
Yes, Intel offers a product comparable to AMD-V and SVM Mode. This product is known as Intel VT-x, which stands for Intel Virtualization. Basically, all you need to do is search for a virtualization-related option in your BIOS, and you should be able to locate one.
What is a Virtual Machine, and what is the meaning of virtualization?
A Virtual Machine is a copy of another operating system that runs on your primary operating system inside a program. It’s not the same as using a completely different operating system, which requires different disk partitioning.
Using Virtual Machine programs like VMWare or VirtualBox, you can run a separate OS inside your main OS. You don’t have to reboot or set up a separate partition to switch between partitions. This is also known as the virtualization of a system to computer geeks.
Virtualization comes in handy in a wide range of scenarios. For example, you could utilize virtualization of your system to run a Mac or Linux Virtual Machine inside a machine operating on Windows OS.
How to access the SVM mode
Depending on the manufacturer of your motherboard, the SVM mode may be buried deep within a variety of different sub-menus.
Proceed through the following steps to access the SVM mode in the BIOS:
For motherboards manufactured by ASUS:
- Restart your computer.
- Press the Delete key continuously until the BIOS menu appears.
- Press the F7 key to access the Advanced mode. There is no need to hit the F7 button on ROG series motherboards because you can go straight to Advanced Mode.
- Select Advanced CPU Configuration from the menu.
- Find SVM mode
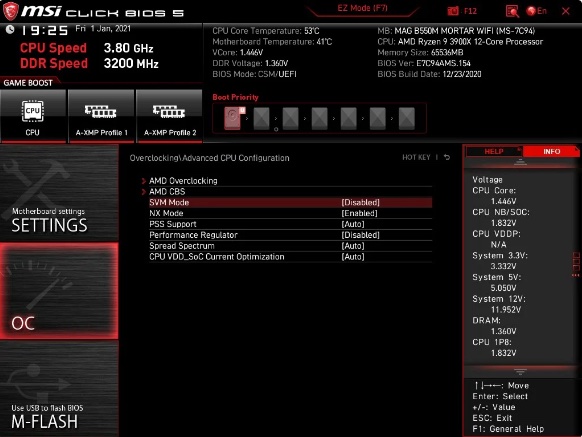
For MSI motherboards:
- Restart your computer.
- Hold down the Del key until the BIOS flash window appears on the screen.
- Select the Advanced option.
- Navigate to that section’s SVM mode.
Access SVM on Gigabyte motherboards:
- Restart your computer.
- Access the BIOS by continuously pressing the Del key until it appears on the screen.
- Select the Advanced option.
- Go to Advanced CPU Settings from the menu.
- Find SVM mode.
Steps to follow on ASRock motherboards:
- Restart your computer.
- Hold down the Delete key until the BIOS menu appears.
- Select the Advanced option.
- Go to CPU Configuration.
- Select SVM mode.
How to Enable SVM mode on your computer
Before enabling SVM to run virtual machines, you need to ensure that your hardware resources are sufficient to run a virtual machine on it.
Unless you execute virtualization operations such as virtual machines or emulators, there is no benefit in enabling SVM. If you turn on SVM while also having the Hyper-V Windows feature turned on, there is a possibility that your system’s performance will suffer slightly.
A virtual machine operates as if it were a distinct computer with an OS. Therefore, for it to function, it needs to have CPU, GPU cores, storage, and RAM, which are taken from the physical system through emulators.
Activating SVM in the BIOS can be done by following these steps:
- Hit the F2 key to open the system’s BIOS screen while your PC reboots.
- Navigate to the Advanced menu > Select CPU Configuration.
- Go to the SVM Mode > Choose the Enable Option from the menu.
- Navigate to the Save & Exit menu > Click on Save Changes.
Why is SVM mode Disabled by default?
By default, SVM is turned off in the BIOS, mostly done for safety concerns. If someone were to infect your computer with vicious malware, and that malware was to find a means to run behind your primary operating system, it would effectively have substantial control over your computer.
Going into the BIOS and turning virtualization on purposefully is required so that you can confirm that you do, in fact, want to activate it.
In what cases SDM mode has to be enabled?
So, at what point exactly should you start giving virtualization of your system some serious thought? Let’s discuss a few such situations when virtualization might be useful.
Virtualization is a technique that is used frequently in server farms and data centers to partition available resources.
For example, if you have ever utilized a service such as Google Stadia or GeForce Now, the video game you are playing is being streamed to you from one of the many virtual machines in a specific server farm.
In situations like this, resources such as the total number of CPU cores are often distributed relatively evenly among the number of active virtual machines (VMs).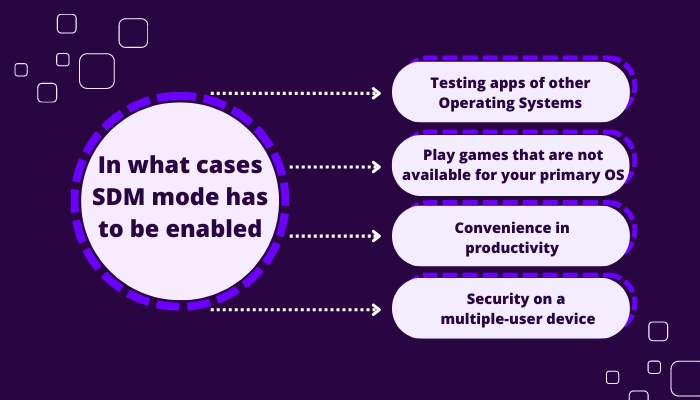
Here are some scenarios in which you should enable SDM on your device:
1. Testing apps of other Operating Systems
You can enable SVM mode on your BIOS for the purpose of testing applications of other operating systems or developing them.
For instance, a virtual machine (VM) running Android or macOS on a Windows computer can significantly assist an Android app developer.
2. Play games that are not available for your primary OS
SVM mode enables you to run other operating systems on your computer without much hassle. Hence, you can enjoy all the apps and games available for the OS you are running on your virtual machine.
If you’re a die-hard PC gamer and want to play a popular Android game that all of your friends are playing but don’t want to use your phone, you can utilize your computer’s SVM menu. You would benefit greatly from using an Android virtual machine (VM) such as BlueStacks.
3. Convenience in productivity
Virtualization of a system in your PC also makes sense for running productivity software compiled for a different operating system.
Let’s say you just made the jump from Mac OS to Windows and are now missing some of your favorite applications from OS X. You will still have access to those programs if you use virtualization, which will save you the time and effort of learning a new process for a new application.
4. Security on a multiple-user device
Virtualization is the solution for you if you require something more secure than Windows User Accounts or users who need various operating systems.
It is designed for situations in which numerous persons use the same computer. However, you should preserve the performance of your hardware by utilizing a solution like Unraid, If you are going to run virtual machines on your PC.
Performance impact of enabling virtualization
If you enable virtualization on your computer, the performance of the rest of your PC, even when it is operating regularly, should not be affected. This is because the virtual machine itself uses the computer’s resources.
However, there are conflicting claims concerning whether virtualization options consume additional performance or cause minor problems when activated.
As a result, I wouldn’t advocate using virtualization when it isn’t being actively utilized because of these concerns.
But how does the Virtual Machine’s performance compare to that of an OS installed in the physical system?
This can vary depending on several different factors. Still, generally speaking, because Virtual Machines have very limited or even no direct access to the underlying hardware, there is a significant performance penalty associated with running something inside of a VM as opposed to not using virtualization at all.
Emulation and virtualization share some similarities, but virtualization and emulation are not the same things at all. This is just one of how the two concepts are similar.
In contrast to emulation, which uses software to simulate hardware, virtualization focuses more on creating an independent operating environment for a different OS. This environment is assigned some or all of the hardware resources available on the host machine.
Compared to the expense of emulation, the performance overhead brought on by virtualization is relatively insignificant.
First things first, check to see if your computer has a processor made by Intel.
You must ensure that either the Intel VT-x or another Virtualization option is selected in the Intel BIOS if you are working with an Intel CPU and motherboard.
If you are working with an AMD CPU, you might hear it referred to as AMD-V rather than SVM Mode.
Essentially, you need to search for the right BIOS option to enable virtualization on your computer.
Is a virtual machine less powerful than the physical system it is running on?
Yes. To begin with, virtualization will inevitably, by its very nature, introduce some overhead.
It is difficult to determine an exact amount since it can vary based on many circumstances. Still, you should anticipate at least a performance deficit of 5 percent for both your central processing unit and your memory. However, this shortfall shouldn’t accumulate for every virtual machine (VM).
Depending on the solution, virtual machines can operate in a startling manner similar to the hardware they emulate.
Using Unraid, for instance, it is possible to turn a single personal computer into two or more computers by partitioning the resources that are accessible. This is good enough at utilizing the hardware used for gaming purposes.
Conclusion
The SVM mode is a useful tool for operating virtual machines on your computer. It enables additional functionalities that would be unavailable to you otherwise.
You can run numerous operating systems, a variety of emulators, and other software simultaneously.
However, you should employ caution when using it. If you don’t do that, it could make things difficult for you.