Graphics Processing Units (GPU) are meant to aid a computer’s CPU in accelerating graphics rendering. However, while helping a computer’s graphics operation, GPUs can also be a matter of concern for the owner.
Are you worried about your GPU overheating under minimal load or while idling? Or, do you want to know the trick to understand whether your GPU is overheating or not?
You have come to the right place for this information.

In this article, I take a deep dive into the reasons that cause GPU overheating and solutions for these conditions. So keep reading till the end to find the solution for your situation.
Normal temperature range of GPUs
The normal working temperature of GPUs range from 40 degrees Celsius to 90 degrees Celsius, which is significantly higher than the room temperature defined as 20 to 25 degrees Celsius.
For this reason, your GPU might always feel warm, even when it’s not operating under a heavy workload or idling. However, if the GPU temperature exceeds 90 degrees Celsius, it’s not automatically given that your GPU would show overheating symptoms.
That said, it is always advised to regulate GPU temperature under 80 degrees Celsius for optimal performance.
| Temperature Range (o Celsius) | Remarks |
|---|---|
| 28o - 50o | The GPU is idling |
| 50o - 90o | GPU is handling tasks according to its capability. |
| Above 90o, | Thermal throttling is going to kick in. More cooling is recommended. |
Related content you should read about what is a Good Idle GPU Temp?
Why is my GPU getting hot?
A GPU is essentially billions of transistors connected in a circuit that the clock signal operates.
As with all other electronic circuits, processing units too has some internal resistance, which causes some amount of power loss. This power loss results in heat, for which the processing unit’s performance gets hampered.
The main reasons for GPU overheating are given below:
Overclocked GPU
Each computer processing unit has a preset clock speed which determines how many operations per second the unit is capable of. Overclocking means setting the clock speed more than the rated speed to increase the number of operations per second.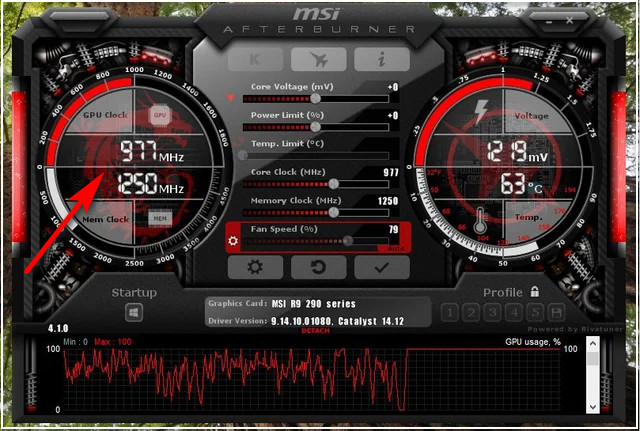
Overclocking is a very popular way of enhancing GPU performance. Even some manufacturers package their components with rated overclocking features for heavy-duty users.
But such a performance enhancement method has some problems too. Because increased performance means increased power consumption, which results in increased heating of the GPU.
Related guide on is CPU or GPU More Important for Gaming?
Ongoing background processes
Graphics intensive software for 3D model rendering, photo or video editing, etc., uses GPU power juice for processing tasks.
If your computer has graphics-intensive tasks running in the background, that will make the GPU work more even when you are not using the software currently. Consequently, the GPU gets heated while graphics-related processes run in the background.
Limited fan speed
Every GPU has a cooling system attached to them which helps to keep the balance between GPU performance and temperature. Many such schemes have a default setting of turning off the cooling system if the GPU temperature is below a certain level.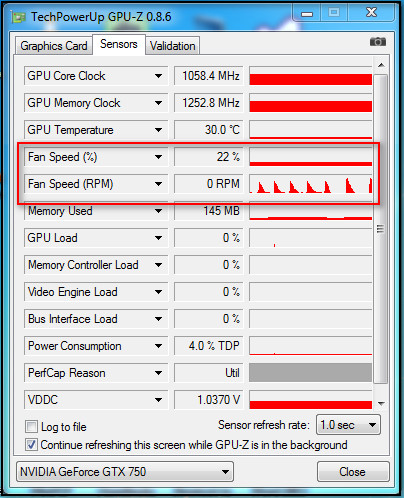
For example, if the GPU coolers of your computer were programmed to switch off when the GPU temperature is under 45 degrees Celsius, the fans would stop cooling the GPU if it operates under 45 degrees Celsius.
Although this cooling management is a handy feature to reduce power consumption, stopping the coolers entirely can assist with heat buildup inside the computer.
Some more guides on why are GPU Prices so High?
Dusty heat sink
The GPU of your computer is always connected with heat sinks to increase thermal stability. The large metal body of the heat sink spreads the heat generated by GPU, hence controlling the device’s temperature.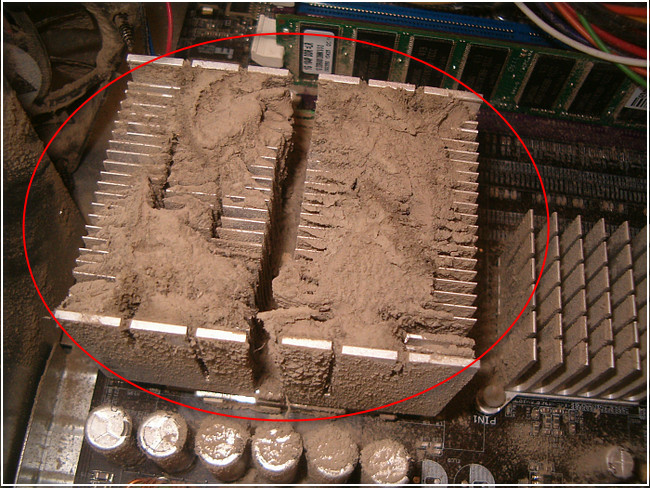
Usually, desktop GPUs would have larger heat sinks compared to laptop GPUs due to the difference in their performance category and power consumption.
Dust accumulation on heat sinks is a common reason for GPU overheating and overheating the entire system.
Deterioration of thermal compounds
Thermal compounds are used to interface a heat sink with a heat source such as a CPU or GPU. Usually, such compounds are liquid solutions that are electrically insulating but have thermal conductivity.
Such thermal compounds remove air pockets between the heat sink and the source. This increases thermal conductivity, allowing the heat sink to dissipate more heat.
But like other good things in life, thermal compounds also deteriorate with use and time. Faulty thermal paste interfacing a GPU and a heat sink would cause GPU overheating.
Also related to this guide about how to fix GPU not Detected in BIOS Issue?
Insufficient airflow
Although this is the most common reason users suffer from overheating issues, there are many reasons for which a computer might not get sufficient air for its components.
Clogged air vents and dusty cooling fans can obstruct airflow inside the computer casing. Hence, the temperature of the GPU gets increases.
Unstable power supply
As mentioned before, some percentage of a GPU’s consumed power results in thermal loss due to the internal resistances of the component.
The GPU takes its power from the power supply unit of the computer. If a power supply unit is faulty and supplies more than the rated voltage to the GPU, further power loss happens in the form of heat. So a power supply which sends more than rated voltage to a GPU would cause GPU overheating.
Read more on how to Check if GPU is Working Properly?
How to resolve GPU heating issues
If you have found out the issue for which the GPU is overheating, you have already done half of the work. GPU overheating can be eradicated by controlling various factors.
Here are some methods to resolve GPU overheating problems:
1. Remove background apps
Removing graphics-intensive tasks from background processes can help reduce GPU problems.
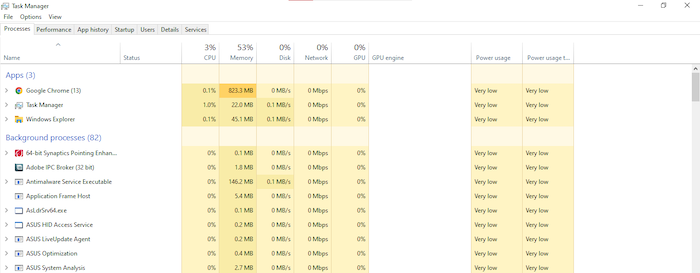
If the GPU of the computer is overwhelmed with operations, it is more likely to overheat due to the extra pressure. You can limit and end such background processes by going to the task manager and disabling or ending those processes.
2. Disable overclocking
Most performance-heavy users overclock their GPU to enhance performance. But as discussed before, this causes the GPU to overheat.
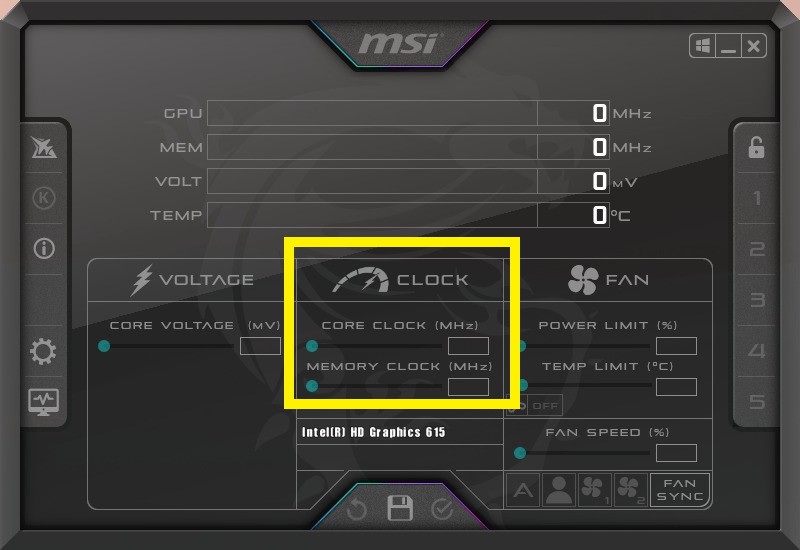
Reset the clock speed of your GPU by sliding the GPU speed to the default factory value. MSI Afterburner is a great tool for controlling GPU clock speed. If the graphics card is factory overclocked and is now overheating, consider resetting the factory setting to lower clock speed.
3. Improve airflow inside the computer
To ensure that any component of your computer is not suffering from extreme heat, you must consider how air flows inside your computer’s casing.
Clean all the vents and air intakes of the casing if you see they are clogged. Dusty fans can cause dust accumulation inside the case, obstructing airflow. Clean all the air circulation paths inside the computer casing to improve airflow and reduce heating caused by the GPU.
4. Tweak GPU fan settings.
If the GPU fans are programmed to turn off when the temperature value is under a certain threshold, that can cause GPU overheating due to prolonged use.
To control fan speed at lower temperatures, you can use the MSI Afterburner.
The steps for tweaking GPU fan settings are given below:
- Launch MSI Afterburner software.
- Go to Settings > Click on the fan tab and select user-defined control.
- Return to the main screen and Uncheck the automatic fan control box.
- Move the fan speed slider from left to right according to your need.
- Save the settings.
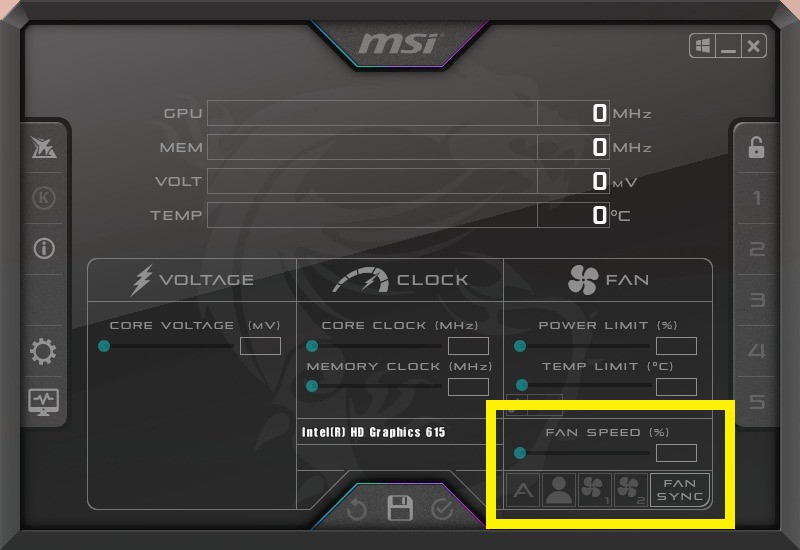
Setting up a custom fan curve is also possible in the MSI afterburner.
5. Replace the thermal compound.
The thermal paste used to interface the heat sink and the GPU deteriorates with time. Replacing the old thermal paste with new ones would help the heat sink to get a larger contact area with the GPU. Consequently, more heat would be transferred from the GPU to the atmosphere, making it cool.
Always be cautious not to damage any pins or components while removing the old thermal paste and applying new ones.
6. Clean the heat sink
The heat sink is designed to have a large surface area to spread the heat it collects from the GPU in the atmosphere. But this large surface area is prone to dust cumulation, which reduces the thermal conductivity of the heat sink.
Properly cleaning the heat sink and ensuring proper contact between the GPU and the heat sink can reduce GPU temperature significantly.
7. Regulate power supplied to GPU
As discussed before, the increased voltage at the input of the GPU causes overheating. This happens when the PSU fluctuates its supply to the components. Therefore, replacing the PSU or regulating the voltage at the GPU input to make it constant would help to reduce heat generation.
FAQs
Q: What are the GPU overheating Symptoms?
Touching the Graphics card would be the go-to solution to understand whether the GPU is overheating or not. But touching the device itself is not always possible. Here are some indications that you should consider while checking for GPU overheating issues:
- Increased fan noise
- Glitches in operation: such as a frozen screen
- Rendering errors in 3D or 2D graphics work
Q: How to monitor GPU temperature?
There are several ways of measuring GPU temperature. This can be checked by the task manager by following these steps:
- Go to task manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc).
- Click on the Performance tab.
- Select GPU from the left column
You will find the temperature, usage and other GPU-related statistics on that page.
Conclusion
GPUs are one of the most powerful processing units that a computer has. They help the CPU in graphics-intensive work so that the tasks given can be finished in a short time. However, such power can be a matter of concern, especially if the GPU is not cooled properly.
I hope you know what might be causing your GPU to overheat and how to solve the issue. Always be careful before removing and inserting the GPU into the motherboard if you are dealing with a laptop.