Most of the time, you can get to your operating system without going to BIOS. But BIOS access is required for changing several important settings, such as the loading priority of boot drives, RAM XMP profiles, enabling virtualization, etc.
Therefore, sometimes you need to change the BIOS to perform specific tasks. But you can’t access it if your PC won’t boot to BIOS.
In this article, I address the issue of PCs not booting into BIOS and how to resolve them.
So, without any further ado, let’s dive into the topic.
Why my PC won’t boot to BIOS?
Your PC won’t boot to BIOS if you have the fast booting startup process activated on your system, your computer will not boot into the BIOS. This is because the fast booting startup process is meant to be fast, preventing BIOS access.
Basic Input Output System (BIOS) is a firmware built into the chip on the motherboard of a PC. BIOS includes a POST test that checks for any hardware problem during startup and loads the boot loader so your operating system can start.
Another possible explanation for your PC not booting into BIOS is that your computer failed the Power-On Self-Test (POST), which indicates a problem with your computer’s hardware.
Here is a list of potential reasons for your PC not being able to boot to BIOS:
1. Fast startup
The fast startup functionality benefits your Windows system in several ways, including that it helps Windows boot up faster than it would with a typical startup.
However, the first startup feature may not always have a positive impact, especially in certain circumstances.
When the Quick Startup option of your system is turned on, it will block the BIOS startup function, preventing your system from booting into BIOS.
You must turn off the fast startup feature on your Windows PC to resolve any problem with the BIOS booting. You may access the BIOS menu by turning off the fast startup feature on your computer.
Stopping the quick startup option may be done in many ways. The first and most straightforward of which is through the System Control Panel. You may quickly disable the fast boot function that allows for a quick startup by navigating to the Control Panel in Windows on your computer.
2. CMOS malfunction
On your computer’s motherboard is a section of memory known as CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor). This is where the BIOS software is stored, ensuring that your BIOS loads correctly.
If the CMOS on your computer becomes corrupted, the BIOS will become unusable, and your PC will not boot correctly.
3. POST Error
The first thing a computer does when it turns on is run a self-test called POST to see if there are any hardware problems. Every time you power your PC on, the POST sequence will run.
To see if you’re experiencing a POST issue, check if your computer is getting any power. A single beep or a series of beeps, some short and others long, can be heard. A power light may be all you see if you don’t hear anything. It’s also possible that your computer’s fans are whirring, but nothing else is happening.
In that case, it is most likely that your PC has some hardware issues, and the computer cannot boot. Hence, booting to the BIOS is impossible, as the subjected computer faces POST issues.
4. BIOS driver issues
The BIOS Driver is the first piece of software that runs when you turn on your laptop or PC. It is thought to be the most essential piece of software in your system as a whole.
Most of the time, the BIOS Driver is on a chip on the computer’s motherboard. It gives all hardware a quick check before startup. It is also what loads your operating system, like Windows, from your hard drive.
If your computer can’t get into the BIOS when it starts up, it could be because the BIOS drivers are outdated.
How to fix a PC not booting into BIOS issue?
Users may occasionally be required to access or enter BIOS to enable a system feature, modify system settings, or troubleshoot a particular error issue on their computer.
However, several Windows users have complained that their computers have experienced issues regarding a PC not being able to boot to BIOS.
In this section, we will go over some tried-and-true solutions to the problem that your Windows PC has booting into the BIOS.
Follow the steps to fix the PC not booting into the BIOS issue:
1. Disable quick startup
Once Fast Boot has been activated, you will not be able to enter the BIOS configuration when the computer is going through startup. The “Press F2 to open Setup Utility and F12 for Boot Menu” prompt will not appear during the boot process.
If you have Fast Boot enabled and want to get into the BIOS setup, hold down the F2 key, then power on your computer. Doing so will get you into the BIOS setup Utility.
Moreover, you can also disable the fast boot option to be able to boot your computer to BIOS. The ways of disabling quick startup vary, but the methods remain the same on Windows 10 and 11.
Follow these steps to disable fast boot from your computer’s Control Panel:
- Press Win + S or click on the magnifying glass icon at the left corner of the taskbar to access the Search bar.
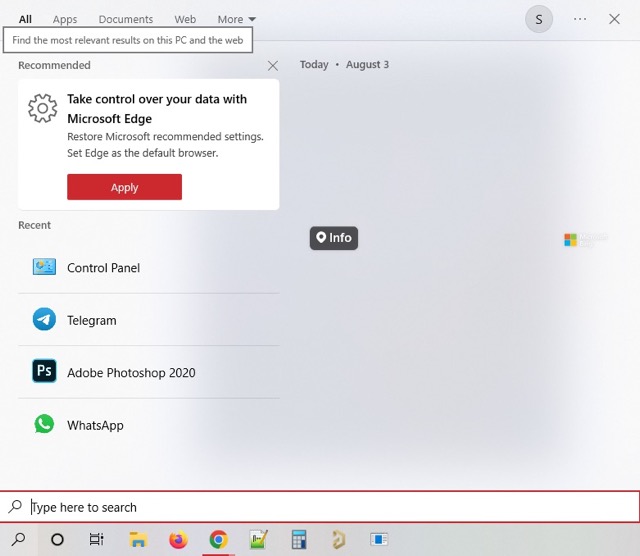
- Type Control Panel > Hit Enter.
- Click on the View by section > Select Category.
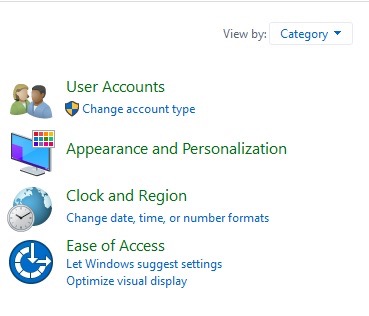
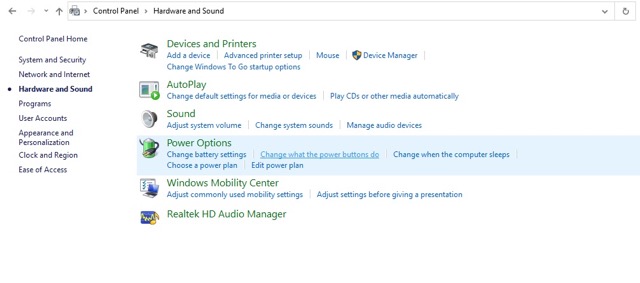
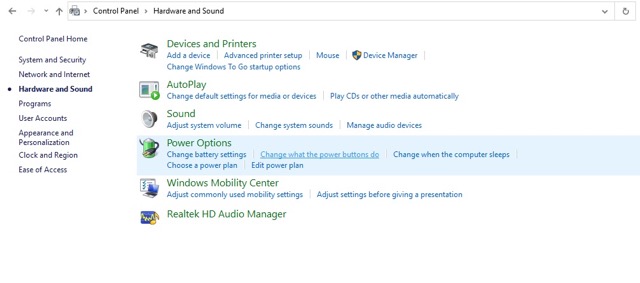
- Go to Hardware and Sound.
- Navigate to Power Options > Click on Change what the power buttons do.
- Click on Change settings that are currently unavailable.
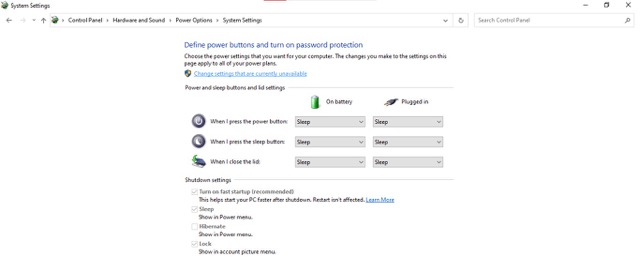
- Uncheck the box beside Turn on fast startup (recommended) in the Shutdown settings section.
- Click on Save changes.
Finally, restart your PC, and see whether you get access to the BIOS menu from the startup prompt.
2. Resolve POST issues
If the BIOS detects a problem when attempting to boot the PC, an error message known as POST code will appear on the screen.
Various POST codes are available, and each means different stages of hardware checking. Hence, each code means a different hardware malfunction stage.
POST-related problems can cause your computer to be unable to boot to the BIOS. To resolve POST issues, you have to consider a lot of factors.
You will most likely have to disassemble the physical components, which is too risky for someone without any experience handling such delicate electronics. Seeking professional help is very recommended if the task seems intimidating.
3. Reset the CMOS
The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) settings are stored in a small amount of memory on a computer’s motherboard called complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS). For example, it holds the commands concerning how to start up and control the keyboard, etc.
There are two ways of resetting the CMOS memory:
- Use a CMOS or dedicated jumper on the motherboard, usually near the battery. The position of the jumper, how long to wait, and where to put the jumper all depend on the motherboard.
- Remove the battery.
Here we will learn about the Battery removal method of resetting the CMOS on a motherboard.
Steps to use in the battery removal method to reset CMOS:
- Turn off all devices connected to the computer that isn’t part of it.
- Remove the power cord from the AC power source.
- Take off the cover of the computer.
- Look on the board for the battery. The battery can be placed in a horizontal or vertical holder or wired to a header on the board.
- Detach the battery connectors.
- Wait for one to five minutes, then put the battery back in.
- Cover the computer again.
- Reconnect the computer and all other devices.
After reassembling your computer, try to access the BIOS from the boot prompt to see whether the issue has been resolved or not.
4. Use UEFI firmware settings to access the BIOS
UEFI firmware settings can also be used to access your system BIOS. To do this, open the Advanced startup window and use the UEFI Firmware settings to quickly make your Windows system boot to BIOS.
Here are the steps to boot your computer to BIOS via UEFI firmware settings:
- Press Win + I to go to Settings.
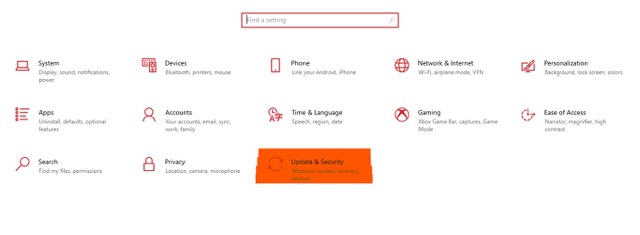
- Select System > Go to Update & Security.
- Select Recovery from the left pane
- Navigate to Advanced startup > Click on Restart now.
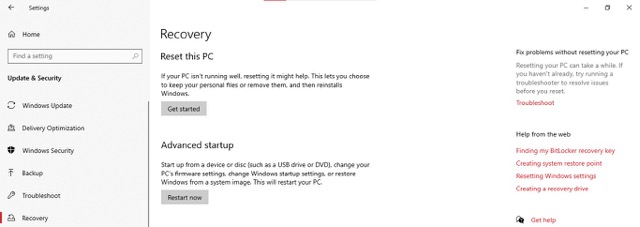
- Click on Troubleshoot from the Advanced startup menu.
- Go to Advanced Options from the list.
- Click on UEFI Firmware Settings.
Clicking on UEFI Firmware Settings will boot your device to the BIOS.
Conclusion
When your computer starts up, if you can’t get into the BIOS, it could be because the drivers aren’t up to date. You can also turn off the fast boot option to get to BIOS without reinstalling all operating systems on your PC’s hard drive.
Moreover, resetting the CMOS memory can resolve this issue. You could also use the UEFI Firmware settings to speed up the time it takes for Windows to get to the BIOS.