Computers have many kinds of memory devices connected to them to function properly. They are called primary memories and secondary memories.
Memory devices like the RAM, cache memory, and register are called primary memory. On the other hand, storage devices like ROM, HDD and SSD are known as secondary memory. They all work in unison so that your computer can run any process.
Have you been wondering what the difference is between RAM and ROM?
You can find all you need to know about these primary memory devices and their differences in this guide. It has all been clearly discussed so that it is easy for you to understand.
So, go through this guide to learn all about RAM and ROM and their differences.
Also, check out our separate post on how to ship RAM safely.
What Is RAM?
Random Access Memory, or RAM, is a primary memory device in your computer. It is volatile, which means that data in it is erased when you shut down your computer. Because of this, it is also called temporary memory.
RAM stores data electrically by the use of transistors. So this means that if there is no electric current, there is no data on RAM. For this reason, data does not exist in RAM if your computer is not turned on.
Since it is a primary memory, RAM can be directly accessed by your computer’s CPU.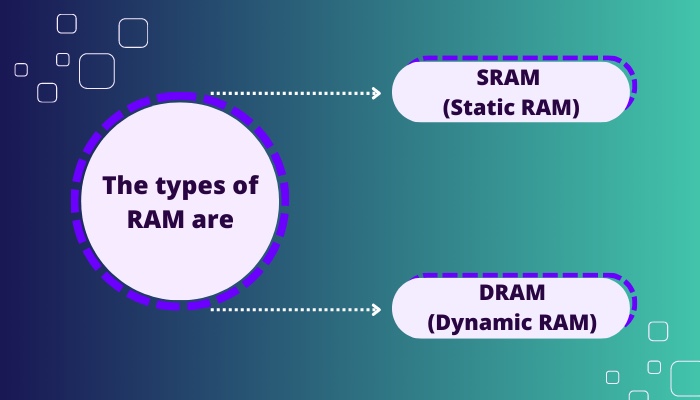
There are two kinds of RAM based on the technology used to store data in them. The types of RAM are
- SRAM (Static RAM): In SRAM, data is stored in memory cells consisting of six transistors.
- DRAM (Dynamic RAM): DRAM stores data using a transistor and capacitor pair to constitute a memory cell.
Both these kinds of RAM store one bit of data in a memory cell.
What is RAM used for? The purpose of RAM in your computer is elaborated on in the next section of this guide. Take a look at it to know what RAM does.
Go and check our other article on can I use two different brands of RAM.
What Are The Functions Of RAM?
The purpose of RAM is to load data from your secondary memory onto it to allow the CPU to access that data to run any process directly. To start a program on your computer, first, it has to be loaded onto the RAM before it can start running for you.
CPU in your PC cannot access the storage device directly. Programs stored in your computer must be copied onto the RAM for the CPU to read those files and run the program.
RAM is both readable and writable. This means that data can be sent from the RAM to the CPU and vice versa. The CPU uses this privilege to read and write data on the RAM to maintain the files it will run and process.
Your operating system is taken to your RAM before your PC can start running. RAM also takes other files related to the apps and programs you run on your computer.
Check out our recent article on is ADATA RAM good.
What Is ROM?
Read-Only Memory, or ROM, is a type of secondary memory present in computers. It is also called permanent memory or fixed memory because it is non-volatile. This means that data exists on it regardless of whether your computer is turned on or off.
ROM contains permanent and important data. The CPU has to access that data continuously, and that data has to be read by the RAM first before the CPU can access it.
In ROM, data is stored in memory chips only once after its manufacture. That data stays in the ROM for the whole of its lifetime. So, it doesn’t matter if your computer is turned on or not, as ROM does not store data electrically.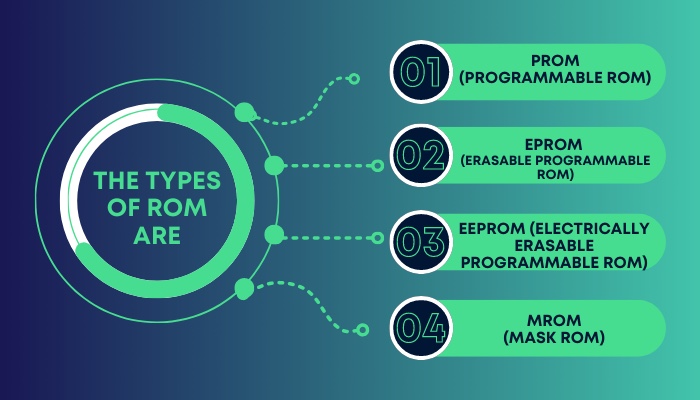
ROMs are of different types based on their storage technology. The types of ROM are
- PROM (Programmable ROM): This kind of ROM can be programmed by a certain kind of device after it has been manufactured.
- EPROM (Erasable Programmable ROM): The content required to be stored in the ROM has to be programmed into it. This content can be erased by exposing the ROM to strong UV rays.
- EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM): This ROM stores the content in electrical circuits, and data can be stored and deleted from it using those special electrical circuits.
- MROM (Mask ROM): The content of this ROM is programmed during manufacture. None but the manufacturer alone can program this kind of ROM.
So what is a ROM used for in your computer? The purpose of this kind of memory is explained in the following section. So, check it out to learn about the usefulness of ROM.
Here’s a complete guide on why is only half of my RAM usable.
What Are The Functions Of ROM?
ROM functions as a storage device for important data like the bootstrap program, firmware for your computer to interact with other devices, video game files on cartridges for consoles, etc. This data is written on it once it has been produced and stays on there permanently.
ROM is only a readable memory. This means that your CPU can only read the data from them. It is impossible for your CPU to write data onto ROM.
Although some ROMS allow you to modify the data in them using certain devices, that data otherwise cannot be changed or deleted ever. So, ROM usually contains important data that the CPU needs to read all the time without changing it.
An example of ROM is the BIOS chip on your computer’s motherboard. It is accessed by your CPU every time you turn on your computer.
You should now have some idea about the differences between RAM and ROM by getting to know about them and their functions. A clear comparison between RAM and ROM has been made in the next section to show their differences comprehensibly.
But before that, go through our epic guide on black screen after installing new RAM.
What Are The Differences Between Computer’s RAM and ROM?
RAM and ROM are inherently very different when it comes to their basic structure, storage capabilities, readability and writability, functions, etc. The differences are simply presented here in a comparative format so that it is easily legible for everyone looking to know about the dissimilarities.
Here are the notable differences between RAM and ROM:
| RAM | ROM |
|---|---|
| RAM stands for Random Access Memory. | ROM stands for Read-Only Memory. |
| It is a primary memory. That means it can be directly accessed by the CPU. | ROM is a kind of secondary memory because it cannot be directly accessed by the CPU. |
| Data is stored electrically using transistors. | Data is stored on memory cells in binary code without the use of any electricity. |
| RAM is volatile memory. It does not retain any data if there is no electric current, i.e., data is removed from it when you shut down your computer. | ROM is non-volatile, which means that data is permanently stored in it. It does not depend on any sort of electric current to store data, so it doesn't lose data when you turn off your computer. |
| RAM is also known as temporary memory. | ROM is also called permanent memory. |
| Data can be both read and written on RAM. | Data can only be read from ROM. |
| Software and other files are loaded on the RAM for the CPU to access and run those files. | ROM contains important data like firmware, bootstrap programs, etc., necessary for your computer to run properly. These files need to be loaded onto the RAM first to run them. |
| RAM has a very fast reading and writing speed. | The rate of reading data from ROM is lower than that of RAM. |
| The storage capacity of RAM is higher than that of ROM. RAMs can have capacities of up to some gigabytes. | ROMs do not have as much storage capacity as RAM. Their storage size is usually a few megabytes. |
| RAMs generally have a high cost. | ROMs are usually less expensive than RAM. |
| Examples of RAM: Cache memory, primary memory for the CPU, etc. | Examples of ROM: BIOS chip, CMOS chip, microcontroller firmware chip, etc. |
Conclusion
RAM and ROM are both computer memories, but they are also essentially very different from each other when it comes to their structure, ability to store data and functions.
When you go through the discussions in this guide about RAM and ROM, their functions and their differences, you will have a clear idea about these two important memories that are crucial for making your computer run correctly and their distinctions.