Have you ever wondered how your PC is booting and how the hardware component collaborates with the operating system software?
Well, all the process starts from the BIOS. After checking the hardware, it provides instructions to connect with the OS.
It plays the most important role in turning on the PC. Yet many users don’t know where the BIOS is and how to access them. Therefore, I’ll share where you can find and access the BIOS.
So, let’s begin.
Where is BIOS Stored in Your Computer?
BIOS or Basic Input/Output System is stored on the motherboard in a non-volatile memory or ROM (Read Only Memory). In modern computers, the BIOS is stored in a flash memory chip that can be rewritten to update with newer versions and fix bugs.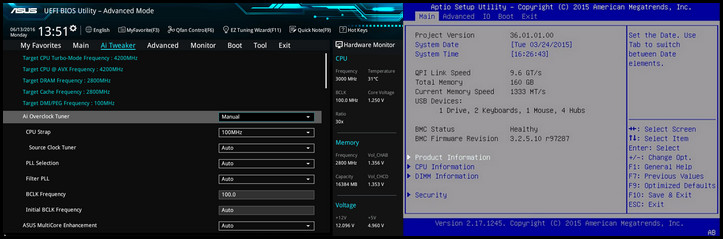
It’s responsible for checking and initializing hardware components. BIOS is also liable for booting up the operating system (OS) of a computer.
There are two main types of BIOS: Legacy and UEFI.
- Legacy BIOS: It’s the older type of BIOS found in the older motherboard. It has a maximum of 2.1 TB storage capacity, but the boot time is slower. The security features are very basic and less flexible compared to newer versions.
- UEFI BIOS: It’s the latest type of BIOS that is available for all the current motherboards. There’s no storage limit, and the boot time is very fast. The security system is very strong and flexible for different operations.
If you’re unsure about your BIOS type, you can read our separate article to check if your BIOS is Legacy or UEFI.
The BIOS is stored in a separate type of storage compared to the regular storage drive. As a result, the data remains intact if anything happens to your computer or storage.
How Does BIOS Work?
BIOS performs different tasks, but most importantly, it boots your PC or laptop.
When you turn on the computer, the microprocessor requires instructions to load the operating system. The BIOS provides the necessary instructions to the microprocessor and loads the OS from the hard drive.
The BIOS is located closer to the processor. So, the instruction execution time is very short, and the PC can boot up quickly.
It was not possible to boot up the computer without BIOS. Including this, BIOS completes a series of important tasks during the startup.
- Power-on Self-Test (POST): Before booting the operating system, the BIOS checks if the hardware components function properly before booting the operating system. This includes the CPU, memory, storage devices, and other components.
If every component works correctly, the BIOS gives a green signal. Otherwise, it will indicate a POST issue and beep through the motherboard. - Hardware Initialization: When the POST process completes, it goes to the next stage and prepares the hardware for the OS to take control.
- Bootstrapping: The BIOS loads a small boot loader program from the hard drive or SSD. It is responsible for loading the operating system (OS) into memory.
Once the operating system is loaded properly, the BIOS concludes its process and gives control over the OS. The operating system then initializes the rest of the system task.
How to Access BIOS Settings
The easiest way to access the BIOS settings is by using the BIOS key during the startup. For most computers, the buttons are ESC, Del, F2, and F10. When turning on the computer, you’ll see the BIOS button name on your screen for a second. Pressing the BIOS key will enter you into the settings.
Based on the manufacturer and type, the interface and settings may differ. Here are some of the BIOS variants:
- American Megatrends (AMI) BIOS
- Award BIOS
- Phoenix BIOS
- Insyde BIOS
- Gigabyte UEFI BIOS
- ASUS UEFI BIOS
- MSI UEFI BIOS
- ASRock UEFI BIOS
After that, you can access the advanced BIOS settings and alter various options. It will let you change the boot order, system date & time, hardware settings, security settings, overclocking, etc.
Ending Note
BIOS is one of the crucial parts of a computer. To preserve it from external damage, it has a separate storage.
You will find the BIOS chip or storage in your motherboard near the processor. This location gives BIOS the best way to communicate with the CPU and other components.
Goodbye!