Starlink is the world’s first and largest satellite constellation. It uses a low Earth orbit to deliver broadband internet that can support streaming, online gaming, video calls, and more. It gives people worldwide access to high-speed broadband internet with low latency.
But is the technology ready to roll out for everyone on planet earth? Are the infrastructures capable enough to deal with the increasing worldwide need for internet bandwidth?
In this article, I go through all the details about what Starlink is trying to achieve and give my opinion on whether or not they are still in their beta testing phase. Let’s dive in!
What Is The Beta Phase of An Upcoming Technology?
Tech services still in the beta phase will, in most cases, experience some speed or performance concerns, and the corresponding software will be riddled with flaws. The goal of beta testing is to minimize disruptions caused to users, and it frequently includes testing the product’s usability.
The process through which a beta version is delivered to customers is referred to as a beta release. It is often the first time the service is made available to users who are not affiliated with the organization that developed it.
Some services are maintained in what is known as “perpetual beta,” which means new features are regularly added to the software without establishing a definitive “stable” release.
Companies have started to use the term beta less strictly as a direct result of the Internet, making rapid and inexpensive software distribution significantly more feasible.
The developers may choose to release either a closed or open beta version of their product. Closed beta versions are sent to a limited number of users invited to participate in a user test. In contrast, open beta testers come from a bigger group or anybody interested.
The product may be eligible for private beta testing if it can give value but is not yet ready to be used by everyone. This may be the case if there are problems with scaling, a lack of documentation, or the software still lacks essential functionality.
The testers document any bugs they encounter and may also offer suggestions for extra features they feel should be included in the final product.
Open betas serve two purposes: to demonstrate a product to prospective customers, and to test the product with a large user base, which is more likely to unearth unknown faults than a much smaller testing team would be.
Also, check out our separate post on does Starlink internet have data caps or limits.
IS Starlink Still in Its Beta Version?
At the end of 2021, the Starlink internet services beta phase, established by Elon Musk’s company, SpaceX, was rolled out to the market. These services were designed for both personal and commercial use. According to the organization’s most recent report, as of June 2022, it serves 500,000 clients throughout 36 different nations as subscribers.
Yes, the Starlink internet service is still in beta testing, and many functions have not yet been implemented. In this section, I will discuss why Starlink is still in its beta testing phase.
Here are some reasons for which the Starlink internet service is still considered in its beta test phase:
1. Not Being Stable And Fully Operational
According to Starlink’s FAQ page, the beta test version subscribers have to pay USD 99 and will receive data speed from 50Mb/s to 150Mb/s, with the latency as low as 20 to 40 ms. But they also declared that there might be “brief periods of no connectivity at all.”
This implies that regular update and maintenance work will occur while users are connected to the Starlink internet, which may result in the temporary unavailability of the service. This is an indication of Starlink still being in its beta testing phase.
Here’s a complete guide on Starlink VS HughesNet all you should know.
2. The Starlink Satellite Constellation Is Not Yet Complete
As of September 2022, Starlink comprises more than 3,000 small satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO) that talk to transceivers on the ground.
This many satellites might seem like a lot at first, but if you look at SpaceX’s plans, you’ll get an important insight. In the first stage, Starlink satellites got permission to launch 12,000 satellites into Low Earth Orbit (LEO). 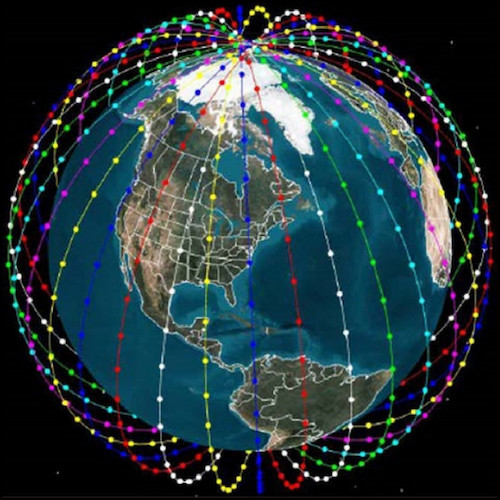
For the Starlink internet to work well, there must be as many satellites as possible. For example, if a satellite needs some maintenance or update, backups can help keep your connection uninterrupted.
Also, in October 2019, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) of the United States sent paperwork to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) on behalf of SpaceX to get spectrum for 30,000 more Starlink satellites.
So, the company has a long way to go before they finish putting their plan into action, so the service is still in beta.
Go and check our other article on Starlink for gaming-is it good or bad.
3. Complications Regarding Getting Permission From Various National Authorities
Regulations imposed by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and long-standing international treaties necessitate that the respective country jurisdictions grant landing rights before satellite services can be provided over any nation-state.
Consequently, even though the Starlink network has near-global reach at latitudes below 60 degrees, broadband services can only be delivered in forty nations as of September 2022, with applications pending in many more countries.
As the company’s goal is to reach every country globally, it can be said that they are still; in the beta phase of rolling out their services.
4. Lengthy Delivery Period
Customers who were discussing their orders on Starlink’s Reddit page in 2021 began to discover that the estimated arrival dates for their orders had been moved back by one full year, to the period starting in late 2022 and ending in early 2023.
After it became clear that these delays would occur, Starlink modified the frequently asked questions part of its website so that it now includes a question about when clients might anticipate receiving coverage.
According to it, “silicon shortages have delayed production, which has harmed our capacity to fulfill orders.” “We ask that you navigate to the Account page to view the most up-to-date estimation of when you can anticipate having your order completed.”
Silicon shortages had supposedly thrown Starlink back by a full year in several regions, despite Musk’s earlier anticipated that a statewide rollout would be completed by October 2021. This is indicative of a service in its beta testing phase.
How Does Starlink Internet Work?
In a paper in Wireless World magazine titled Extraterrestrial Relays in 1945, famous science fiction author Arthur C. Clarke wrote about how a satellite standing relatively still on a region of the earth can potentially be used for communication. 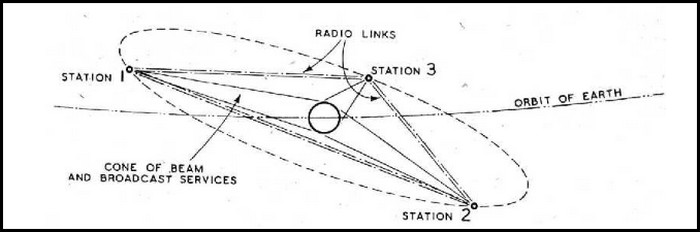
Since Sputnik 1’s debut in 1957, geosynchronous COMSATs in geostationary orbit have provided rudimentary satellite internet services.
Using satellites to connect to the internet is a simple concept. To transfer data over the internet, a satellite system employs radio signals to travel through empty space instead of cables like fiber optics.
In this system, signals are transmitted from ground stations to orbiting satellites, which then transmit the data back to Earth. So, Clarke referred to them as ET Relays.
Up until now, the primary source of satellite internet has been a single geostationary satellite in Geostationary orbits, 35,786 kilometers above Earth. 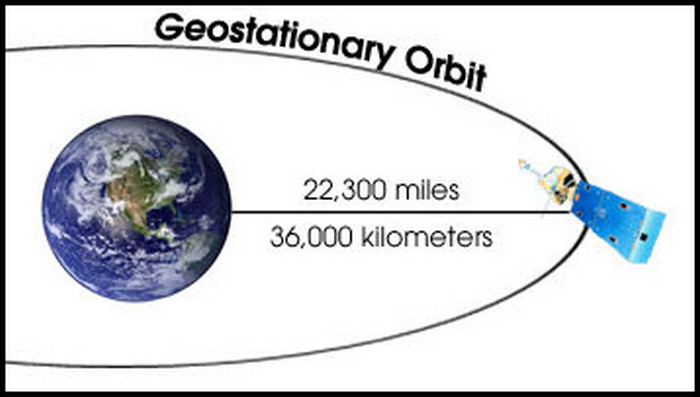
The high latency (the time it takes for data to travel between a user and a satellite) caused by this enormous distance makes it difficult, if not impossible, to support streaming, online gaming, video conferencing, and other high data rate activities.
Starlink is a network of hundreds of satellites that circle the Earth at an altitude of roughly 550 kilometers (this orbital distance is referred to as “Low Earth Orbit” or “LEO“), providing coverage in every region of the world.
Compared to other networks, Starlink’s latency (about 20 milliseconds) stands in stark contrast at 600 milliseconds or more. Each Starlink satellite has a flat shape and weighs 573 pounds. Up to sixty satellites can be carried by a single SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
Follow our guide step-by-step to find out if Starlink is available in your area.
Conclusion
Starlink is a revolutionary company already serving many people across the globe with its high-speed broadband satellite internet. But similar to other great products, developing such services takes time.
Starlink is still implementing its plan by adding more and more satellites to its constellation and applying to countries for regulatory permission. Although the network is still in its beta phase, eventually, the service will be available for all to use.