Hyperthreading is the most wanted feature that a high-end PC builder seeks in the processor. If you are thinking about speed and efficiency in a processor, you will find these two factors in a hyperthreaded CPU. Intel and AMD are the two giants in the CPU market, offering top-tier processors to consumers. Meanwhile, they are mainly focused on manufacturing CPUs that can surpass their previous gens.
Intel and AMD are the two giants in the CPU market, offering top-tier processors to consumers. Meanwhile, they are mainly focused on manufacturing CPUs that can surpass their previous gens.
Hyperthreading is an Intel technology, and AMD doesn’t support it.
But the question remains! Does hyperthreading work, and is it worth it?
To know the answer, I had to dive deep into the core of hyperthreading technology. I have gathered all the required info and poured it into this article to inform you about hyperthreading, including its pros and cons.
So, read on till the end.
What is Hyperthreading and Why Should You Care?
HyperThreading is a hardware-based technology that allows more than one thread to run on each core. It can handle more work parallelly than a non-hyperthreaded CPU. The CPU exposes two execution contexts per physical core when you active hyperthreading.
You need hyperthreading to process more information in less time and run more background tasks without interruption. You can split highly intensive work into two cores with a hyperthreaded processor.
Moreover, hyper-threading can easily handle heavily loaded works like gaming and video editing.
It’s a virtual core; this tech makes one core work like two cores. The heavy work is split into several threads on a single core, which makes the processing power even faster.
Hyperthreading reduces idle time by running applications between the virtual cores, but the idle time is high in a single-threaded core.
Additionally, hyperthreading allows the user to load multiple programs simultaneously and speeds up the time it travels.
Lastly, to put it in a word, you will need hyperthreading when you have to multitask a lot, such as in gaming and video editing. The main goal of hyperthreading is to increase the number of independent instructions the CPU can handle.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hyperthreading
Hyperthreading features have both pros and cons. To know every aspect of hyperthreading, you must know its bad and good sides.
Let’s start with the good side of hyperthreading first. Before going to the analysis, let’s look at the main advantages and disadvantages of HyperThreading in a table.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Better Performance | Can’t Solve Insufficient Core Problem |
| Resolving Cache Misses | Software and Hardware Independent |
| Reduce Idle Time | Increases CPU Temperature |
| Facilitates Switching Between Threads |
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of hyperthreading:
Advantages of HyperThreading
Better performance, less idle time, accurate branch predictions and facilitating switching between cores are the main benefits of hyperthreading. Plus, hyperthreading resolves the chances of missing cache while running an application. But the main fact is the performance will boost significantly.
Here are the advantages of hyperthreading:
1. Better Performance
Boosted performance is the most significant advantage of hyperthreading. With all the virtual cores, you will find it’s faster than the non-threaded processor. When running a quad-core CPU, this technology tricks programs into thinking the CPU is octa-core.
All the CPU-intensive programs will run faster due to less execution time. Moreover, you can perform multitasking without putting too much pressure on the CPU. That’s why gamers and video editors always use a hyperthreaded processor.
2. Resolving Cache Misses
Cache missing happens with a non-threaded CPU. The cache mainly misses when a CPU, system or app tries to access data from its cache, but the data is missing itself.
When the data gets scattered across different parts of memory, the CPU uses RAM to access data to complete the data acquiring process. But accessing the RAM takes a long time, so the CPU core becomes idle.
Hyperthreading resolves this issue by involving one core to retrieve the data and the second core to execute the task.
3. Reduces Idle Time
Hyperthreading helps to reduce idle time. When the CPU can’t perform parallel execution, some execution unit has to wait for its turn, which refers to idle time.
Sometimes the CPU must wait for the main memory for source data for executing operations. Meanwhile, the CPU can’t do anything until it receives the data and remains idle.
Hyperthreading involves virtual cores to perform all the operations parallelly to reduce ideal time.
4. Facilitates Switching Between Threads
For multitasking, you must need multicores to run all the applications smoothly. That’s where hyperthreading facilitates you. As you know, a thread is a virtual version of the actual physical core. So, hyperthreading doubles the exact amount of the physical core.
Hyperthreading creates more threads within the CPU and makes it more efficient.
This feature makes the CPU more efficient by quickly switching the executable resources between threads. To be precise, hyperthreading can run programs like games in the front and several other apps in the background.
5. Resolves Branch Misprediction
The branch predictor is actually a circuit in the CPU that predicts the direction of a branch before it goes in a definite direction. Branch prediction makes the execution time faster by predicting the fastest route for the process.
When the branch predictor fails to predict a branch, the overall process starts from the beginning. And this results in a delay in the execution time. So, hyperthreading handles a task by its virtual cores.
While the first thread waits for the core to resolve misprediction, the second thread deals with the execution using the resources.
Disadvantages of HyperThreading
There are several disadvantages like software and hardware dependency, temperature rise and inability to handle tasks just like the physical core. Some apps won’t benefit from hyperthreading. Plus, you will find high temp while running tasks.
Here are the disadvantages of hyperthreading:
1. Can’t Solve Insufficient Core Problem
Hyperthreading can’t compete against actual physical cores because it only creates more threads inside the same core. This technology enables only virtual cores within a physical core.
But the virtual core isn’t beneficial for some apps that mainly rely on actual cores. So, you won’t notice any performance improvement in some apps when hyperthreading is turned on. Not only that, CPUs are core dependent too.
2. Software and Hardware Dependent
By hyperthreading, you can see performance improvement in some specific apps because those are designed that way. Designed that way means those apps execute all the tasks in parallel. So execution time is faster than a non-hyperthreaded CPU.
But not all the apps are designed to work in parallel mode, and some apps need to execute tasks in serial. That’s when you won’t see any performance boost by hyperthreading.
Not all the CPU supports hyperthreading because it’s a hardware-related feature. So, the downside is hyperthreading is software and hardware-based.
3. Increases CPU Temperature
Turning on hyperthreading may result in high CPU temperature. This happens because more threads will run to execute all the tasks in parallel mode.
Some apps entirely rely on the per-core performance, just like PC games. Some games may run faster when you disable hyperthreading. Due to multi threads working simultaneously with the physical core, a temperature rise becomes obvious.
But multi threads mainly facilitate when you perform multitasking and heavy multicore workloads. Multithread uses more power to juice up all the cores, and that’s when the temperature rises.
What CPUs Can Use Hyperthreading?
Intel’s most processors come with Hyperthreading technology. Along with Intel’s server-based processor, Xeon and Intel’s core i3, i5, i7 and i9 have hyperthreading tech. Hyperthreading is a trademark and technology of INTEL though AMD has a similar technology named Clustered Multithreading.
For example, Intel’s core i9-10900K is a 10-core-based CPU with 20 threads when you enable hyperthreading. With the two logical cores, the performance will boost significantly more than a traditional single-threaded CPU.
But for AMD Ryzen CPUs, you will find Clustered Multithreading technology similar to Intel’s Hyper-Threading. AMD uses only cluster-based architectural design instead of block-based because it performs better with its higher number of cores.
AMD’s Ryzen 3, 5, 7 and 9 have Clustered Multithreading technology. Their top-tier product Threadripper has more cores and threads than any Ryzen series.
So to say more precisely, most of the Intel CPUs have hyperthreading technology, but AMD follows their own Clustering Multithreading tech.
How to Tell if My CPU Allows Hyper-Threading?
If your CPU allows hyperthreading, the number of logical processors doubles the number of actual cores. So, If your CPU has four cores, you will find eight logical processors. To check, you will need to go to the Windows Task Manager and check numbers for both cores and virtual processors.
So, all you need to check is whether the logical process is double the actual core count or not.
Here are the steps to check if your CPU allows hyperthreading or not:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to launch Task Manager.
- Click on the Performance tab.
- Click the CPU from the left pane.
- Look for Cores and Logical processors beneath the graph.
- Check out the processor number for both of them.
![check-logical-processor-number-from-task-manager]](https://10pcg.com/wp-content/uploads/check-logical-processor-number-from-task-manager.jpg)
If the Logical processor number is double the number of Cores, your CPU allows hyper-threading. But your CPU doesn’t allow hyperthreading when both numbers are the same. Moreover, hyperthreading will turn on by itself when your CPU has it.
How Good is Hyperthreading?
Hyperthreading tricks the programs into thinking there are two cores instead of one. This feature doubles the number of physical cores, and if you are a multitasker, it will boost the application’s performance. Virtual processors can use the maximum efficiency of a single core.
So, if you run an application programmed to execute all the tasks in parallel mode, hyperthreading will use virtual cores to perform the task faster.
Mainly, hyperthreading has two advantages. One is – it provides more hardware threads so that when an application needs more threads to handle the operation, it provides non-engaged hardware threads.
The second advantage is that each core can run a thread simultaneously when a task is parallel enough. It also enables better utilization of hardware resources.
Turning off hyper thread will boost performance in some applications because threads bounce around less. But, you will surely benefit from hyperthreading if you render or edit videos.
Speaking of gaming and streaming, you will see stable and higher FPS in 4 core/8 thread processors than in a 4 core/4 thread. You will gain 15-18% better improvement in a hyperthreaded CPU than in a non-hyperthreaded CPU.
Does Hyperthreading Affect Performance?
Hyperthreading or simultaneous multithreading (SMT) improves performance when running an application that needs multiple threads to handle all the tasks in parallel. As you know, not all software can facilitates by hyperthreading. So, the performance improvement is entirely dependent on the app.
But with hyperthreading, most of the app’s performance increased by 15-30% depending on the processore and app’s function type. Those softwares which are written in such a way capable of fully utilizing the CPU get highly benefited from hyperthreading.
Yet commercial softwares are not written in that way. Because those softwares have to run on dozens of CPUs. Perhaps you can customize an app for a specific purpose, like a Youtube app. You can design the software to utilize the CPU cores fully. That’s where hyperthreading comes to play.
So, whether hyperthreading affects the performance or not entirely depends on how the software handles the tasks.
Is HyperThreading Worth it for Gaming?
You can benefit from hyperthreading if you have a processor with fewer cores because most modern games require more than two or four cores. With hyperthreading enabled, you will get double the number of actual cores, and gaming will improve significantly.
Hyperthreading gives you sufficient cores to simultaneously run applications at the back and gaming. But you can’t expect better gaming on a hyperthreaded CPU than on a higher physical core-based CPU.
However, there are both positive and negative effects while gaming with hyperthreading.
FPS will increase in most of the games. Moreover, you will see smoother gameplay without any lags. If your processor supports hyperthreading, you must enable it before gaming.
The downside is games require GPU power more than CPU. Graphics processing won’t boost up by hyperthreading. Sometimes turning on HT will make your game slow or laggy. It happens because hyperthreading consumes a lot of power, which may negatively affect the game.
Wrongly distribution of the workloads by hyperthreading among the physical and logical cores can slow them down.
So, my suggestion is to play the game and check whether the gameplay improves by hyperthreading or not. If not, turn off the feature and play the game.
Hyperthreading Vs. No-Hyperthreading: Which CPU is Better?
Hyperthreading is applied to applications where multiple tasks are scheduled to avoid idle time on the processor. While gaming, video editing or 3D rendering, the performance will improve significantly for hyperthreading. But some apps might slow down due to this feature. So, it depends on the apps.
When you enable hyperthreading (HT), it will help the CPU to push the light task to background applications to one core and the heavy applications like games and video rendering apps to another core.
Don’t think that Hyper-Threading will increase the processor’s cores; those are just virtual cores. Enabling it will only help to channel the task efficiently into a process. HT lets each core run two threads concurrently.
But non-hyperthreading works in a traditional way for processing the tasks.
Not all apps can work smoothly with hyperthreading. The performance of those apps slows down instead of ramping up due to the HT. Well, some apps only need to complete the task serially, not in a parallel way.
So, it depends on your work which one is better. If you are a multitasker or need to work with heavy applications, you will need a hyperthreaded CPU. Else, you shouldn’t enable the HT or buy a hyperthreaded CPU.
Hyperthreading Vs. Multithreading: Which CPU is Better?
If you want to increase the overall performance, both hyperthreading and multithreading can do that differently. Hyperthreading divides the workload into virtual cores, but multithread doesn’t turn a core into two. Multithreading splits workloads into several sub-processes.
Hyperthreading tricks the program into believing that there are double amounts of physical cores. It improves speed and performance by allowing several threads to run a single core. It pushes the CPU cores to their maximum efficiency.
When hyperthreading is enabled, it divides the CPU into threads and assigns specific tasks to each thread. That’s how HT reduces the overall workload on the CPU.
The truth is neither it increases the performance nor increases the physical cores.
On the other hand, a multithread doesn’t turn a core into two; instead, it divides a program or tasks into multiple sub-processes. And each sub-process is assigned with a specific thread. Multiple threads handle numerous tasks.
So, multithreading creates multiple threads inside each process, but hyperthreading splits a single processor into two separate ones. Moreover, hyperthreading is hardware-related, but multithreading is software-related.
Lastly, both technologies are great from their perspectives. If you are a multitasker or heavy workload-based app user, go for a hyperthreaded CPU or choose a multithreaded CPU for regular tasks like surfing the web, watching movies, light tasks, etc.
How to Turn On & Turn Off Hyperthreading
To turn on & off HyperThreading, you must go to the motherboard BIOS. The steps are quite simple, and all you need to enable this feature.
Note: Before enabling hyperthreading, you must ensure whether the CPU has this feature or not. You can simply search the CPU model name in google and read the specification. If the total threads are double the number of total cores, it supports hyperthreading.
The following steps are applied to an ASUS motherboard. Other brands’ motherboard BIOS UI may differ from this. So, go through the steps carefully.
Here are the steps to turn on & turn off hyperthreading from the BIOS:
- Restart the PC and press the exact key (Example: F2 or Del) to enter the BIOS.
- Click on Advanced Mode from the bottom right corner or press F7.
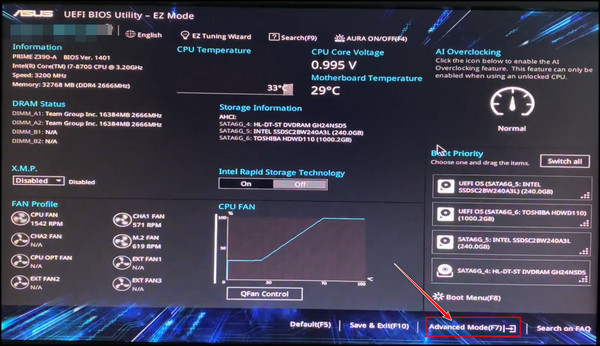
- Go to the Advanced tab > Cpu Configuration.
- Scroll down and look for Hyper-Threading.
- Click on the dropdown button beside Hyper-Threading and choose Enabled.
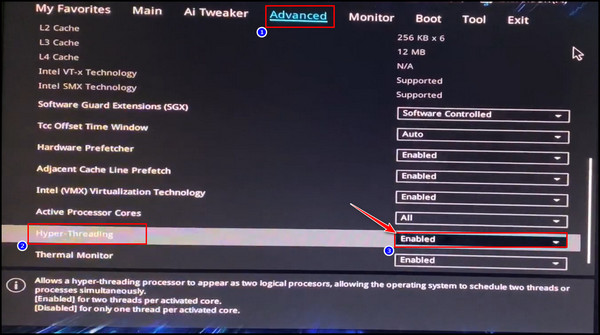
- Click on Save & Exit or Press F10.
Now your PC will restart and launch CMD to check for the hyperthreading activation.
Here are the steps to check whether hyperthreading is enabled or not:
- Launch CMD. Simply press the Win key + R and type CMD in it.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to launch CMD with Admin mode.
- Choose Yes from the prompted window.
- Type Wmic and press Enter.
- Type again or paste the following command line
CPU Get NumberOfCores,NumberOfLogicalProcessors /Format:List 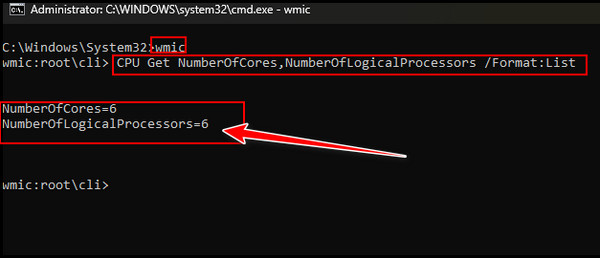
- Press the Enter key again.
If the number of logical processors is twice the number of cores, you have successfully activated hyperthreading. Your CPU doesn’t support hyperthreading when both numbers are equal.
You can also turn off Hyperthreading by disabling it from the BIOS.
FAQs
Should I Use Hyperthreading?
You should use hyperthreading if you multitask all the time or run heavy applications like games or 3D rendering apps. Don’t use it when using the PC only for net browsing or running normal lite apps.
Is Hyperthreading Bad?
Hyperthreading isn’t bad, and performance will improve after enabling it. Games will play without lag, and video editing apps will render videos faster.
Does Disabling Hyperthreading Increase Performance?
Some apps don’t get boosted from hyperthreading. Instead, they get slowed down because those apps don’t execute tasks in parallel. They only execute tasks one by another by maintaining a serial. So, disabling hyperthreading will increase performance for specific apps.
Wrapping Up
Hyperthreading has become the main priority for gamers. Many gamers found that the FPS has increased and remains stable after they enabled hyperthreading. Moreover, the animator and video editor can render videos faster after turning on HT.
So, hyperthreading is worth it, from my point of view. But if you are an average PC user or have a robust higher core-based processor, don’t go for it.
So, from my point of view and analysis, hyperthreading is worth it. What is your opinion?
Let me know in the comment box. Peace out!